National Flag

National Map
National History
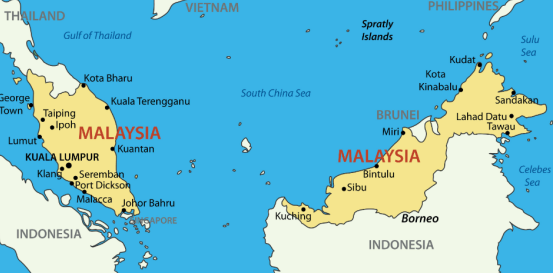
Located in Southeast Asia, the land is separated into the east and west by the South China Sea. West Ma lies in the south of the Malay Peninsula, bordering Thailand in the north, Singapore across the Johor Strait in the south, the South China Sea in the east and the Strait of Malacca in the west. East Horse is located in the northern part of Kalimantan, adjacent to Indonesia, the Philippines and Brunei. The total length of a national coastline is 4,192 km. It is a tropical rainforest climate. The average annual temperature is 22-28 ℃ and the coastal plain is 25-30 ℃.
At the beginning of AD, the Malay Peninsula had ancient countries such as Capricorn swing and Wolf tooth repair. TheKingdom of Manraa, centered on Malacca in the early 15th century, unified most of the Malay Peninsula. Since the 16th century, it was occupied by Portugal, the Netherlands and Great Britain. It was completely made a British colony in the early 20th century. Sarawak and Sabah were historically Brunei, and they became British protectors in 1888. During World War II, the Malay Peninsula, Sarawak and Sabah were captured by Japan. Great Britain resumed colonial rule after the war. The United Malaya state declared its independence on August 31,1957. On 16 September 1963, the United Malaya State of Malaya merged with Singapore, Sarawak and Sabah to form Malaysia (Singapore withdrew on 9 August 1965).
Malaysia is a democratic federal state with a constitutional parliament, whose political system is inherited from the British Westminster system. Due to historical reasons, Sarawak Prefecture and Sabah have greater autonomy.
The Constitution of Malaya was promulgated in 1957 and continued after the founding of Malaysia in 1963, renamed the Constitution of the Federation of Malaysia and revised several times. The Constitution stipulates that the Supreme Head of State is the head of state, leader of Islam and commander of the armed forces, elected by the council of rulers for a term of five years. The Supreme Head of State has the supreme powers of legislative, judicial and administrative powers, as well as to appoint prime ministers and refuse to dissolve Congress. In March 1993, the Malaysian Assembly passed constitutional amendments removing privileges like legal immunity. The constitution was amended in May 1994 to provide that the Supreme Head of State must accept and perform official duties on a government recommendation. In January 2005, the Malaysian parliament again passed the constitutional revision case and decided to transfer the management of water supply affairs and cultural heritage to the central government.
The Malaysian constitution makes the state a constitutional parliamentary democracy for the monarchy. Congress is the supreme legislature, consisting of the House of Lords and the Commons. The House of Commons has 222 seats for a five-year term, eligible for re-election. The current Speaker Nazius Azha, served in September 2020. The House of Lords has 70 seats, with two elected by each of the 13 states and the remaining 44 appointed by the Supreme Council for three-year terms. The current Upper Speaker, Raffles Aden took office in September 2020.
The Malaysian government has not established the post of deputy prime minister, replacing four senior ministers, making it clear that the four senior ministers will share their responsibilities when he is absent.
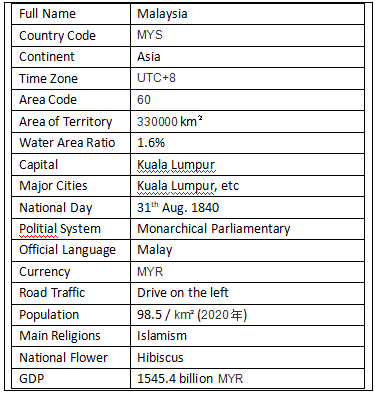
The country is divided into 13 states and three federal jurisdictions. The thirteen states are Johor, Kedah, Kelantan, Malacca, Semelan, Pahang, Penang, Perak, Glass City, Selangor, Dengjia Building and Sabah, Sarawak. There are the capitals Kuala Lumpur, Butra again (Bucheng) and Namuan.
The Supreme Court was established on January 1,1985. It was renamed the Federal Court in June 1994. There are Malaya Superior Court (for West Ma) and Boro State Superior Court (for East Ma), and the states have district courts and inference chambers. There are also special military courts and Islamic courts. Chief Justice Dato 'Tengku Maimun binti Tuan Mat, took office in May 2019, Malaysia' s first female Chief Justice. Attorney General EdrusHaren, appointed in March 2020.
Country Basic Information
Food Industrial Specific Information
Government
Food organizations
Standards, Policies and Regulations
Approval Export List (Traditional Trade)
Approval Export List (Cross border E-commerce)
Approval Export List (FTA Agreement)
Recommended Featured products
Recommended EFLine Members
Export-oriented Exhibition
Import-oriented Exhibition
Comprehensive Exhibition
The Customs Data
Consumption Data
Sales & Marketing Data
EFL Reports
Collective Analysis Reports
Regional Relations
Industry Policy
Supply and demand fluctuation
Force Majeure Events
EFL Reports · Collective Analysis Reports · Bilateral Trade
China and Malaysia have signed more than 10 economic and trade cooperation agreements, including the avoidance of Double Tax Agreement, the Trade Agreement, the Investment Protection Agreement, the Maritime Transport Agreement and the Civil Air Transport Agreement. The Bilateral Economic and Trade Joint Commission was established in 1988. The Bilateral Business Council was established in April 2002. In 2017, the two countries signed the Memorandum of Understanding on Promoting Economic Development through the Chinese Silk Road Economic Belt and the 21st Century Maritime Silk Road Initiative, and the Memorandum of Understanding between the Chinese Ministry of Commerce and the Malaysian Ministry of Communications on Cooperation in the Field of Infrastructure Construction.
bilateral trade between Malaysia and China was RM 315.19 billion, up 0.2% in 2019, according to data released by the Malaysian Foreign Trade Development Authority. Among them, Malaysia's exports to China were RM 139.61 billion, up 0.3%; Malaysian imports from China were RM 175.59 billion, up 0.1%, or 20.7% of the total Malaysian imports. The Malaysian trade deficit was RM 35.98 billion, down RM 50 million from 2018.
In 2019, the growth of Malaysian exports to China mainly resulted from basic products, especially steel products,
LNG, pulp products, palm oil, metalwork, optical and scientific equipment, and processed foods. Palm oil exports to China rose 17.8% in 2019 after seven consecutive year declines. The growth of Malaysian imports from China is mainly petroleum products, transportation equipment and plastic products.
According to Chinese customs statistics, in 2019, bilateral trade between China and Malaysia reached USD 124 billion, up 14.2% year on year, China's exports to Malaysia were USD 52.13 billion, up 14.9% year on year, and imports from Malaysia reached USD 71.83 billion, up year-on-year of 13.6%.
China is Malaysia's largest trading partner, the largest source of import and the largest export destination. Bilateral trade has developed steadily. In recent years, the bilateral trade volume between China and Malaysia has maintained a scale of about $ 100 billion. According to China's statistics, the bilateral trade volume between China and Malaysia was US $ 131.16 billion in 2020, up 5.7% year on year; of which China exported US $ 56.43 billion and US $ 74.73 billion. China has become Malaysia's largest trading partner for 12 consecutive years. Main commodities imported from China include integrated circuits, computers and their parts, brown oil and plastic products; China exports main commodities include computers and their components, integrated circuits, clothing and textiles.
Food Industrial Specific Information · Government
The Embassy in Malaysia
Address: 229, JALAN AMPANG,50450 KUALA LUMPUR,MALAYSIA
Tel.: 00603-21636853,00603-21645301
Email: chinaemb_my@mfa.gov.cn
Business Office of the Chinese Embassy in New Zealand
http://nz.mofcom.gov. cn
Address: 14 Hill Street,Thorndon,Wellington,New Zealand.
Tel: 0064-44714100
Consulate General in Penang (Malaysia)
http://penang.chineseconsulate.org/chn/
Address: 28 B&C,Jalan Tunku Abdul Rahman 10350 George Town,Penang,Malaysia
Tel: 0060-42189795
Fax: 0060-42189798
Email: consulate_chc@mfa.gov.cn
Consulate General in Kota Kinabalu (Malaysia)
Address: Palm Court,Lot 7,No 3,VIP Lot,Lorong Pokok Palma Rajah,Jalan Lintas,88000 Kota Kinabalu,Sabah,Malaysia
Tel: 0060-88385481
Fax: 0060-88385491
Email: chinaconsul_kk_my@mfa.gov.cn
Consulate General in Gucci Jin (Malaysia)
http://kuching.chineseconsulate.org
Address: No. 276, Section 10, Wangchang Waterway, Gujin City, Sarawak State, Malaysia
Tel: 006-082-240344
Fax: 006-082-232344
Email: consulate_kuching@mfa.gov.cn
The Malaysian Embassy in China
Address:No. 2, Liang Ma Qiao Bei Jie, Chaoyang District
Tel. (Tel): 65322531-200
Fax, Fax: 65325032
Email: Email (E-mail):mwbeijing@kln.gov.my)
Food Industrial Specific Information · Comprehensive Exhibition · Exhibition (Food)
Kuala Lumpur Malaysia MIFB
https://www.qufair.com/convention/18355.shtml
Exhibition Date: 07.28 ~ 07.30
Venue: City: Malaysia-Kuala Lumpur-Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
Host cycle: once a year
Exhibition Industry: Food, Beverage
Sponsor: Malaysia Expo International Company Limited
Food Processing Exhibition and Food Packaging Exhibition, Kuala https://www.qufair.com/convention/14946.shtml
Exhibition Date: July 15- 18
Venue: Malaysia-Kuala Lumpur-Kuala Prince World Trade Center, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
Exhibition cycle: once a year
Sponsor: Huaxun Exhibition Co., Ltd.
China Agency: Xiamen Wenxin Exhibition Co., Ltd