EFL · National City (Russia)
Russia

Symbolic construction: The Kremlin

[National name] Russian Federation, also called Russia (Р cidnczoud.
[Area] 17,0982,200 square kilometers.
[Population] There are 194 ethnic groups with a population of 146 million, of which 77.7% are Russian. The main ethnic minorities are Tatar, Ukrainian, Bashkil, Chewash, Chechen, Armenian, Avar, Moldova, Kazak, Azerbaijani, Belarusian and so on. Russian is the official language throughout the territory of the Russian Federation, and each republic has the right to establish its own national language and to use it in conjunction with Russian in the territory of that republic. The main religion is Eastern Orthodoxy, followed by Islam.
[Capital] Moscow (М). It covers an area of about 2560 square kilometers. The resident population is about 12.3 million. Average temperature: January -8℃, July 21℃.
"The head of state" of the Russian federation President, vladimir, base success to Mr Putin, (В л а д и м и р В л а д и м и р о kind guide и discusses some related problems П У Т И Н).
New Year's Day in the Gregorian calendar: January 1; Orthodox Christmas: January 7; Defender of the Motherland Day: February 23; International Women's Day: March 8; Spring and Labor Day (the former Soviet Union Labor Solidarity Day) : May 1; Victory Day of the Great Patriotic War: May 9; National Day (Declaration of National Sovereignty adopted day) : June 12; National Unity Day: November 4.
Russia stretches across the Eurasian continent, 9,000 kilometers from east to west and 4,000 kilometers from north to south. It is bordered by Norway and Finland to the northwest, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland and Belarus to the west, Ukraine to the southwest, Georgia, Azerbaijan and Kazakhstan to the south, and China, Mongolia and North Korea to the southeast. It faces Japan and the United States on the east. The coastline is 33,807 kilometers long. Most of the region is in the North Temperate Zone with a continental climate, and the temperature difference is generally large. The average temperature in January is -5 ~ -40℃, and the average temperature in July is 11 ~ 27℃.
Internal political stability in Russia. On March 18, 2018, Russia held a presidential election and Vladimir Putin won a second term. Putin was sworn in for a six-year term on May 7.
[Constitutional Law] Adopted by referendum on December 12, 1993, and officially entered into force on December 25, 1993. This constitution is the first constitution after the independence of Russia, stipulates that Russia is a republican democratic federal legal system of the country, established the presidential system of national leadership system.
The Council of the Russian Federation (parliament) consists of the Federation Council (upper house) and the State Duma (lower house).
The Government of the Russian Federation is the highest state executive authority. On January 16, 2020, Mr Putin signed an executive order, appoint m schuss jing (М и х а и л В л а д и м и р о kind guide и discusses some related problems М И Ш У С Т И Н) as prime minister.
[Resources] Russia is very rich in natural resources, many types, large reserves, high degree of self-sufficiency. It ranks first in the world in land area. Forest covers an area of 11.26 million square kilometers, accounting for 65.8% of China's total land area, ranking first in the world. Wood stock volume ranks first in the world. The proven reserves of natural gas account for 25% of the world's proven reserves, ranking first in the world. Proven oil reserves account for 9% of the world's proved reserves. The coal reserves rank fifth in the world. The reserves of iron, nickel and tin rank first in the world. Gold reserves are the third largest in the world. Uranium reserves are the seventh largest in the world.
[Economy] In 2019, Russia's GDP grew by 1.3% year on year. As of May 1, 2020, international reserves amounted to US $567.3 billion. Due to international oil price fluctuations, OPEC+ production reduction agreement, weak domestic investment, reduced net export, sluggish domestic demand and other factors, Russia's economy maintains a low growth rate. In 2019, GDP (calculated at current prices) was 110.05 trillion rubles (approximately 1.7 trillion US dollars at the annual average exchange rate of 1 US dollar =64.73 rubles, the same below), with an increase of 1.3%. In 2018, GDP per capita was 707,500 rubles (about $11,000).
Russian Macroeconomic Statistics 2015-2019 (at current prices)
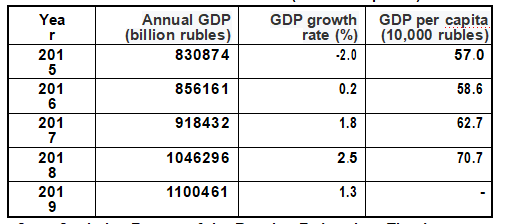
Source: State Statistics Bureau of the Russian Federation. The data are adjusted as of 1 April 2020.
[Foreign Trade] According to the statistics of the Russian Customs Agency, in 2019, Russia's total foreign trade was $672 billion, down 3% year on year, with a surplus of $177.2 billion. Among them, the export was 424.6 billion US dollars, down 6% year on year; Imports reached US $247.4 billion, up 2.7% year on year.
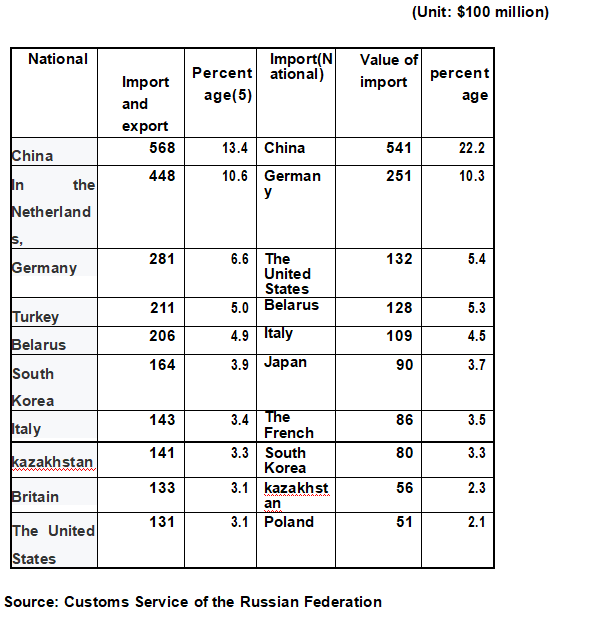
[Major Trade Partners] The top 10 trading partners of Russia in 2019 are: China ($110.9 billion), Germany ($53.2 billion), the Netherlands ($48.8 billion), Belarus ($33.4 billion), the United States ($26.2 billion), Turkey ($26 billion), Italy ($25.2 billion), South Korea ($24.4 billion), Japan ($20.3 billion), Kazakhstan ($19.6 billion). China has been Russia's largest trading partner for ten consecutive years.
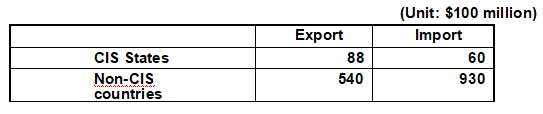
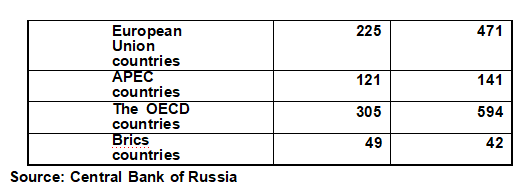
Regionally, the EU remains Russia's largest trading partner. In 2019, Russia's total trade with the EU reached US $277.8 billion, down 5.6% year on year, accounting for 41.7 percent of Russia's total foreign trade in that year. The total volume of trade between Russia and Asia-Pacific countries was US $212.2 billion, down 0.5% year-on-year, accounting for 31.8 percent of Russia's total foreign trade. The total trade volume with CIS countries was $80.4 billion, down 1.7% year on year, accounting for 12.1% of Russia's total foreign trade. Trade with Eurasian Economic Union countries was US $57.3 billion, up 1.1 percent year on year, accounting for 8.6 percent of Russia's total foreign trade.
Russian foreign trade statistics 2015-2019
(Unit: $100 million)
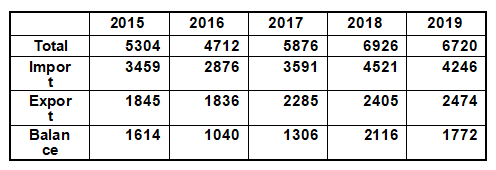
Source: Customs Service of the Russian Federation
Russia's trade with major trading partners in 2019
According to the BP Statistical Yearbook of World Energy, in 2018, Russia was the world's second largest exporter of oil and the largest exporter of pipeline natural gas, accounting for 12.8% and 23.6% of the world's total oil and pipeline natural gas exports respectively. In 2019, the structure of Russia's export commodities did not improve significantly. The export of mineral resources products was US $267.7 billion, accounting for 63.3% of Russia's export volume. Other major export commodities in order: metals and their products 37.5 billion US dollars, accounting for 8.9%; $27.7 billion, or 6.5 per cent, for vehicles and equipment; $27 billion, or 6.4%, for chemical products; Food and agricultural raw materials $24.8 billion, or 5.9%; Wood and its products, $12.8 billion, or 3 percent.
In 2019, mechanical and electrical products were Russia's main import goods, accounting for 46.2 percent of Russia's total import, reaching 112.5 billion US dollars. Other major imports were: chemical products 47.8 billion US dollars, accounting for 19.6 percent; Food and agricultural raw materials $29.9 billion, or 12.2%; Metals and their products $17.9 billion, or 7.3%; textiles and shoes $15.1 billion, or 6.2%; Mineral resources amounted to $5.1 billion, or 2.1%.
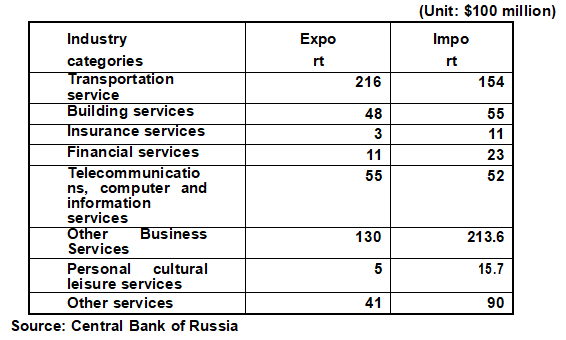
[Trade in Services] According to the statistics of the Central Bank of Russia, in 2019, Russia's total trade in services was $161.8 billion, including exports of $62.8 billion and imports of $99 billion, with a deficit of $36.2 billion.
[Service Trade Industry Structure] In 2019, the main industries of Russia's service trade are shown in the following table:
Industry distribution of Russia's service trade in 2019
[Major Service Trade Partners] In 2019, Russia's major service trade partners are shown in the following table:
Major service trade partners of Russia in 2019
[Bilateral Trade] According to Chinese customs statistics, in 2019, the trade volume between China and Russia was US $110.79 billion, up 3.4% year on year. Among them, China's export to Russia was US $49.74 billion, up 3.7% year on year. China imported US $61.05 billion from Russia, up 3.2% year on year.
China exports to Russia main categories including mechanical equipment and spare parts, electrical equipment and spare parts, furs, and artificial fur products, apparel and clothing accessories, shoes, boots, shin guards and spare parts, vehicles and their zero accessories, plastic products, steel products, such as optical, photographic, medical equipment and accessories, toys, sports products and accessories, furniture, lamps and lanterns, etc.
The main categories of goods imported by China from Russia include fossil fuels, mineral oil and its products, timber, wood pulp and wood products, aquatic products, nickel and its products, ore, slag and ash.
Russian culture
Russia is a multi-ethnic country. Ethnic Russians constitute 79.83% of the population in the Russian Federation, and there are also more than 180 ethnic minorities living there. Russian culture has historically dominated Russia based on Russian and Orthodox Christianity, but this cultural predominance is sometimes incomplete. It should be pointed out that the Slavic countries such as Ukraine, Belarus, Serbia and Poland have played a great role in the development of Russian culture.
Russian culture
Fighting people, bare-handed fighting brown bears, typhoon weather flying planes... There is no sign of Russian bravery. As a great military power, the history of the militaristic old Mao may have a lot to say, but I will simply skip it here. "The body is the capital of revolution." In this respect, the "fighting nations" appear to be well-capitalized. In winter, it is common to see young women walking in strollers on the wooded paths around the Russian residential community. Even though it's minus 20 or 30 degrees, the mothers are exposing their babies' delicate faces and breathing fresh air to acclimatize their babies to the cold. For older children, encourage them to do outdoor activities and develop a brave character through physical exercise. In the street, it is common to see toddlers running and bouncing behind their striding mothers, picking themselves up when they fall. This custom is passed down from generation to generation, so that children from an early age to lay a good foundation for physical fitness. Russia's diet of high protein high calorie, plus the good habit of national sports, so that its physical quality is generally better.
Literature and Art
Secular literature in Russia emerged in the 17th century. The first secular work is The Life of the High Priest Avakum (it is not a religious work, since it is the work of Avakum Petrov himself, and in fact what most people know about his saintly life is the story after his death).
The 18th century produced a number of outstanding poets and writers in Russia. Among them there are wassily terry JiYaKe, А н т и о х К а н т е м и р, Г а kind guide р и и л Д е р ж а kind guide и н, meters high, Romano soff; Н The "freely" livelihood of scinna, scinna, scinna. Playwright Alexander Sumarokov Д Scala is the spena. The main form of literary creation at that time was classicism.
Here are some of Russia's most famous authors:
Fyodor Dostoyevsky: (Russian: Ф The "Hoo-pee" was a Russian writer who began his writing at the age of 20 years old. The first step is the "Hoo-pee", the "Hoo-pee" and the "Hoo-pee". The first novel, Poor Man, was published in 1846 at the age of 25. Among Dostoyevsky's important works are Crime and Punishment (1866), Idiots (1869) and The Brothers Karamazov (1880). Dostoyevsky wrote 11 novels, 3 novellas and 17 short stories, and his literary style had a profound influence on the world literary world in the 20th century.
Leo Tolstoy (Russian: Л е kind guide Н и seem о л а е kind guide и discusses some related problems Т о л с т о й, Latin: Lev Nikolayevich Tolstoy. English: Leo Nikolayevich Tolstoy; September 9, 1828 -- November 20, 1910) was a Russian novelist, philosopher, political thinker, and educational reformer. He was the most influential member of the noble family of Tolstoy. Tolstoy, whose novels War and Peace, Anna Karenina and Resurrection are regarded as classic novels, is considered one of the world's greatest writers. Gorky once said: "He who does not know Tolstoy cannot know Russia."
- Hotspots in the news
(1) Russia's green food seminar held in Beijing agricultural products into the hot topic of the cooperation between China and Russia - the web https://baijiahao.baidu.com/s?id=1564278827302630&wfr=spider&for=pc
(2) China "Russian food hall" urge "sino-russian trade" - China news website https://www.chinanews.com/sh/2015/07-25/7426933.shtml
(3) Russia's delicious food "train" into Chinese business into a hot topic - China news websitehttps://www.chinanews.com/gj/2017/02-04/8140188.shtml
(4) on the area along the "train Russian food tasting first appeared in chengdu at https://www.sohu.com/a/363327473_100123034
Human geography
The Russian Federation, commonly called Russia or Russia, is a federal republican constitutional country composed of 22 autonomous republics, 46 prefectuals, 9 border regions, 4 autonomous regions, 1 autonomous prefecture and 3 municipalities directly under The central government of The federal government. Russia is located in the north of the Eurasian continent, across the two continents, land area of 17,075,400 square kilometers, is the largest country in the world.
The ancestors of the Ross people are the East Slavic Ross tribe. At the end of the 15th century, Grand Duke Ivan III established the Grand Duchy of Moscow. In 1547, Ivan IV called himself Tsar and founded Czarist Russia. In 1721, Peter I renamed the Russian Empire. He embarked on the road of aggression and expansion, annexed many countries in Europe and Asia, and constantly expanded its territory. During World War II, Outer Mongolia became independent from China, causing China to lose 1.73 million square kilometers of territory again, causing great harm to the Chinese nation. The Soviet regime was established after the October Revolution of 1917. In December 1922, the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics was formally established. It became a "superpower" alongside the United States during the Cold War.
After the collapse of the Soviet Union on December 25, 1991, Russia, the largest ally, became independent, inheriting most of the Soviet Union's military power, ranking second in the world in overall military strength and possessing the world's largest nuclear weapons Arsenal. In the international system of "one superpower, many powers", Russia is a powerful country with great influence. Its military strength is strong, especially in aerospace technology, which ranks in the forefront of the world. Russia is also one of the five permanent members of the United Nations Security Council and has veto power over Security Council resolutions. In addition, Russia is one of the five BRICS countries.
(1) Introduction video of tourist attractions St. Petersburg Russia https://www.56.com/u60/v_MTQ1MjY0MDI1.html
(2) is the most beautiful square in the world, Russia's magnificent buildings, like a dream castle kingdom _ good video at https://haokan.baidu.com/v?vid=4736627351794108429&pd=bjh&fr=bjhauthor&type=video
(3) why do you say Russian food safety management strictly _ good video https://haokan.baidu.com/v?vid=10850805733508663117&pd=bjh&fr=bjhauthor&type=video
(4) Russians do not engage in flashy, food safety and quality is good, when can we do the same! - tencent video at https://v.qq.com/x/page/w3206tbp4uk.html
- Latest news
(1) the Russian ministry of agriculture or will be temporarily restricting the buckwheat food information center at http://news.foodmate.net/2021/05/592549.html
(2) Russia's polar bear stand up Catch a moving truck in search of food - the web informationhttps://www.163.com/dy/article/G9FBDLJT0514R9OJ.html
(3) Chinese demand boost Russia agricultural export record - food information center athttp://news.foodmate.net/2021/03/587321.html
(4) for the first time in the history of Russia become a net exporter of agricultural products and food - food information center at http://news.foodmate.net/2021/03/587083.html
- Introduction of Country · Food
[Fishery Resources] Rich in resources, there are more than 3 million large and small rivers and more than 2.8 million lakes in the territory; Lake Baikal is the largest freshwater lake in the world. Fishery resources are quite rich, with a total of 25.8 million tons of biological resources and 23 million tons of fish.
Russian people pay more attention to diet, the variety of dishes rich and colorful, "Russian meal" in the world is very famous, to Russia must taste Russian food. Precious caviar, authentic borscht, and traditional pancakes are all very ethnic. Usually in the Russian table the most common is a variety of meat food, almost every meal will have beef, mutton, steak, sausage and so on.
- Food Standards [State Administration for Market Regulation]
Why do you say Russian food safety management strictly https://haokan.baidu.com/v?vid=10850805733508663117&pd=bjh&fr=bjhauthor&type=video
Russia's food safety and management that is fairly strict - tencent video at https://v.qq.com/x/page/d3203m49rq5.html
Russian food agricultural laws and regulations standard assembly - baidu encyclopedia https://baike.baidu.com/item/%E4%BF%84%E7%BD%97%E6%96%AF%E9%A3%9F%E5%93%81%E5%86%9C%E4%BA%A7%E5%93%81 %E6%B3%95%E8%A7%84%E6%A0%87%E5%87%86%E6%B1%87%E7%BC%96/12388998?fr=aladdin
Russian food safety law and food market regulation - baidu library at https://wenku.baidu.com/view/7c4ed1f99e3143323968934a.html
- Policies and regulations 3.1 What are the foreign trade regulations and policies?
7.1.1 Trade authorities
The Russian government departments in charge of trade are the Ministry of Economic Development, the Ministry of Industry and Trade, the Ministry of Agriculture, the Federal Customs Service and so on.
The main functions and responsibilities of the Ministries of Economic Development, Industry and Trade and Agriculture are to formulate foreign trade policies and administer foreign trade, issue import and export licenses, administer foreign exchange business for import and export, formulate export inspection systems, and examine and approve agreements or conventions concerning foreign trade. The Federal Customs Service carries out the foreign trade administration policies of the Russian government and handles customs duties and customs declarations.
According to the laws and regulations of Europe and Asia, economic union, after Russia join the world trade organization, Eurasian economic union members Russia, belarus, kazakhstan, kyrgyzstan, Armenia anti-dumping, anti-subsidy and safeguard measures of the power and function has been all over Europe and Asia, economic union permanent executive arm, economic commission for Europe and Asia, It shall be responsible for the specific implementation of the work in this field. On April 14, 2017, held in the kyrgyz capital bishkek Eurasian economic union heads of state summit, decided to expand the economic commission for Europe and Asia in the customs management permissions, including approval from the Eurasian economic union close condition of the export goods determine the rules of origin, as well as the provisions in the conditions of the free trade area to carry out foreign economic activities, etc. These mandates were transferred to the Eurasian Economic Commission with a view to the future smooth implementation of the EEU Customs Code. The EEU Customs Code has come into force since January 1, 2018. At present, the Union is actively upgrading the digital level of customs cooperation among its member states, promoting the construction of "single window" and advancing the integration process.
7.1.2 Trade legal system
In Russia, the main trade-related laws are the Law of the Russian Federation on the Principles of State Regulation of Foreign Trade Activities, the Law of State Regulation of Foreign Trade Activities, the Customs Code of the Russian Federation,
Customs Tariff Law, Technical Regulation Law, Federal Law on Special Safeguard, Anti-dumping and Countervailing Measures against Imported Commodities, Foreign Exchange Regulation and Supervision Law, Law on Measures to Protect State Economic Interests in Foreign Trade, and relevant laws and regulations promulgated within the framework of the Eurasian Economic Union, etc.
7.1.3 Relevant provisions on trade management
Since 1991, Russia has carried out a thorough reform of the foreign trade management system, cancelled the monopoly foreign trade management system, all registered enterprises in Russia have the right to engage in foreign economic activities, including intermediary business. After its accession to the WTO, Russia adjusted its tariff and foreign trade policies according to its WTO commitments. At present, the vast majority of commodities have been opened to business except for some commodities which are restricted by licenses and quotas.
[Import Management] Russia's import trade management regulations mainly include:
- Quota management. Russia implements import quota management on edible alcohol, vodka, high explosives, explosives, explosive devices, pyrotechnic products, raw sugar, meat, some dairy products and grain. The allocation of import quotas is mainly carried out through bidding and auction. In August 2019, in order to fulfill the obligations under the Vienna Convention for the Protection of the Atmospheric Ozone Layer and the Montreal Protocol, the then Prime Minister of the Russian Federation Dmitry Medvedev signed a government decree to impose temporary restrictions on the import of ozone-depleting substances. According to the Order, Russia adopted temporary quantitative restrictions on imports of ozone-depleting substances on September 7, 2019 and December 31, 2019. The Ministry of Natural Resources of the Russian Federation is responsible for allocating quotas for imports of ozone-depleting substances to applicants. Starting from January 1, 2020, Russia will no longer implement quota management on pork imports, instead imposing a unified 25% tariff.
- License management. The import license system shall be applied to the following two categories of commodities. The first category belongs to special commodities, including chemical pesticides, industrial waste and code-breaking equipment. The second category belongs to the commodities, technologies and scientific and technological information that need to be imported in accordance with the special procedures stipulated by the President and the Government of Russia, including weapons and ammunition, nuclear materials, radioactive raw materials, precious metals, precious stones, narcotics, tranquilizers, dual-use materials and technologies, and individual raw materials and equipment that can be used in the manufacture of weapons and equipment.
(3) Product identification and certification. The sale of imported goods without instructions in Russian is prohibited in Russia. For alcoholic products, audio-visual products and computer equipment and other products, it is forbidden to sell products without security marks and statistical information strips.
For chemical biological agents, radioactive substances, production wastes and some products imported to Russia for the first time, especially food, national registration is required before importation; Imported products for industrial, agricultural and civil construction purposes shall be subject to identification of epidemic prevention.
In January 2005, the Customs of the Russian Federation issued the "List of Imported Products Subject to Compulsory Certification". After several revisions, it stipulated that the import of animals and plants and their products, food, alcohol and non-alcoholic beverages, textile raw materials and their products, machinery and equipment, audio and video equipment and other parts of the imported products were subject to compulsory certification.
Currently, Russia is implementing the electronic tagging system for different categories of goods. Starting from July 1, 2020, a mandatory electronic labeling system will be implemented for tobacco, shoes, medicines and other goods, including locally produced and imported goods. Photographic equipment, fur products, perfumes and other products will also be compulsory by 2020.
[Export Administration] Regulations on export trade administration in Russia mainly include:
(1) Export quota and export license. Russia implements export quota and license management for products that are limited in quantity as stipulated in international agreements, some special products involving national interests and three types of products with large domestic demand. The allocation of export quotas is mainly carried out through bidding and auction. In case of surplus quota, additional issuance may be made according to actual export performance. Should take the goods of an export license, including: wildlife, medicinal herbs, decoding device, weapons, explosives, nuclear materials, radioactive materials, precious metals, your precious and semi-precious stones, mineral resources and ore deposit information, narcotics, mental reagents, toxic substances, some can be used to make weapons and equipment of raw materials, equipment, technology, information, etc.
At present, the Russian government is studying the implementation of quota management for the export of ferrous metals, scrap metals and other commodities.
(2) To exercise supervision over the export of dual-use products. Export licenses are required for the export of dual-use products and technologies, which are issued on the basis of whether the exported products conform to the relevant international obligations undertaken by Russia.
(3) Unified verification system. Russia has a unified verification system for the quantity, quality and price of its exports, but since March 1996 this system is no longer mandatory. At present, only petroleum, refined oil, natural gas, coal, black and non-ferrous metals, wood, mineral fertilizer and other products are verified. The above procedure does not apply to food, veterinary products and shell products. The quarantine and licensing of such products are the responsibility of the national quarantine and health departments.
7.1.4 Inspection and quarantine of import and export commodities
Russian import and quarantine system for all kinds of animal and plant products, according to published on January 9, 2008, no. 1 on the approval of the animal and plant health supervision bureau exercise state on distribution of animals, animal products, animal drug, feed and feed additives, should check products import, export and transit license administrative regulations of the functions of command, Examine the import and export documents of the goods to be inspected, and make a decision to issue or refuse the import license of the goods to be inspected.
Seeds and planting materials of agricultural, forestry, medicinal and ornamental crops, plants and their parts (scion, lamination, bulb, rhizome, tuber, root tuber, potted plants, mushrooms with cut flowers, etc.); Fresh vegetables, fruits and berries; Food, forage, and industrial use of grain and its processed products (rice, rice, walnut, peanut, flour, rice, granular, coffee, cocoa, nuts and dried herbs, tobacco raw materials and ingredients, tea, semi-finished products, malt sugar, spices, coconut meat, cake, cake, cotton, linen and other plant fiber), and animal hides and hair, etc.; Fungi, bacteria, viruses, nematodes, mites, insects and vectors that are harmful to plants and plant products; Insect specimens, plant pathogen specimens and wax leaf specimens of the seed collection; Plant products in mail and passenger luggage; Containers, packaging materials (except synthetic materials), wood and processed products (finished, semi-finished and spare parts), undisturbed soil samples and soil specimens; Feed, ligustilian compound feed and bedding material for animals from the area to be inspected.
Quarantine articles permitted to be imported from Russia must have an import quarantine permit issued by the Russian Federation Agriculture and Food State Phytosanitary Service. The port of entry through the Russian border and the conditions for the import and use of these quarantine objects shall be indicated in the permit. The phytosanitary certificate issued by the phytosanitary and plant protection authorities of the exporting country shall be attached to each batch of quarantine objects. The phytosanitary certificate shall be attached to the waybill of the consignment. Except for countries without corresponding authorities, the sanitary condition of the quarantine object is required to comply with the provisions of the import quarantine license.
[Animal Quarantine] In March 2006, the Russian government promulgated the decision (No. 159) on the implementation of animal epidemic prevention measures when live animals enter the territory of Russia, which stipulates that, prior to the adoption of the Law on Technical Adjustment of the Russian Federation, some live animals and animal products enter the territory of Russia, Comply with the provisions of the existing animal epidemic prevention regulations of the Russian Federation that do not contradict the International Terrestrial Animal Health Code issued by the International Office of OIE of the World Organization for Animal Health. In addition, the requirements of the Terrestrial Animal Code referred to in article 1 of the Decision will be followed in the event of a conflict between the existing Russian Federation regulations on animal epidemic prevention and those of the World Trade Organization.
The Russian Federation can only import the goods subject to inspection from exporting enterprises inspected by the State Department of Veterinary Health of the Russian Federation and included in the list of enterprises that can be exported to the Russian Federation.
[WTO Commitment] According to Russia's WTO Commitment, the sanitary and animal and plant quarantine measures adopted by Russia must be based on international standards and meet the requirements of adequate scientific demonstration and risk assessment. If the level of protection stipulated by Russia is higher than that stipulated by international standards, Russia is entitled to impose more stringent requirements. In this context, Russia will actively participate in the development of standards and recommendations of relevant international organizations. Ensure transparency of procedures: Importers can lodge complaints about suspension, cancellation or refusal of licences for goods under import supervision and receive a written reply stating the reasons for the decision and action taken. Prior to the import suspension, the Russian Veterinary and Phytosanitary Service is obliged to provide the exporting country with the possibility of taking corrective measures accordingly. This commitment does not apply to situations where there is a significant risk to human and animal health. Russia will ensure that its laws in the field of technical standards comply with the requirements of the WTO Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade. Russia will develop technical standards in accordance with international standards and recommendations and under conditions that guarantee the necessary level of safety.
7.1.5 Customs management rules and regulations
Customs administration of the Russian Federation shall be governed by the Customs Service of the Russian Federation in accordance with the Customs Code of the EEU,
Customs Regulation Law of the Russian Federation, Customs Tariff Law of the Russian Federation and other relevant laws and regulations are implemented.
[Management System] Since January 1, 2010, the customs union of Russia, Belarus and Kazakhstan has been officially launched. The three countries implement unified import tariff rates for goods entering the customs territory of the union. For export goods, each country sets export tariff by itself according to its national conditions and needs. On July 6, 2010, the Customs Code of the Customs Union came into full force in Russia, Belarus and Kazakhstan, and the three countries formed a unified border on July 1, 2011. On January 1, 2015, the EEU was officially launched, and on January 1, 2018, the EEU Customs Code was formally implemented, while the Customs Code of the Customs Union was abolished at the same time. The EEU Customs Code unifies the customs administration of the member states of the EEU, including Russia. It provides for the implementation of "electronic declaration", "single window" and "authorized operator" systems.
[Import Tariff] Since the Russian Federation joined the WTO in 2012, the level of import and export tariff committed by the Russian Federation is bound by WTO rules. According to the latest statistics of the WTO, in 2017, Russia's simple average final tax rate is 7.6%, among which the tariff rate of agricultural products is 11.2%, and the tariff rate of non-agricultural products is 7.1%. In 2018, the average MFN rate promised by Russia to WTO members was 6.8 percent, of which the tariff rate for agricultural products was 11.2 percent and the tariff rate for non-agricultural products was 6.1 percent.
A total of 9.8% tax items of Russian agricultural products promised zero tariff, but only 3% of the tax items actually achieved zero tariff. The final tax rate of 43.3% items is less than 5%. Items whose tariff rate is greater than 50% account for 2.5% of the total. In addition, 22.9 per cent of tax items are subject to non-ad valorem duties. For non-agricultural products, 14.2% of the tariff items promised zero tariff, but only 3.4% of the tariff items actually achieved zero tariff. The final tax rate of 51.4% is less than 5%. Items whose tariff rate is greater than 50% account for 0% of the total. In addition, 7% of items are subject to non-ad valorem duty. After Russia joined the World Trade Organization, it has made corresponding adjustments to import and export tariff and tariff quota standards.
Russia imposes import tariffs at different rates on different types of countries.
The rate indicated in the tariff table is the basic rate. Tariffs are levied at the basic rate on goods imported from countries enjoying MFN treatment; Tariffs are levied at twice the basic rate on goods imported from countries that do not enjoy MFN status.
Countries of the Commonwealth of Independent States that have signed free trade agreements with Russia and developing countries that have been approved by UNCTAD to enjoy the GSP can enjoy tariff preferences in Russia. Among them, imports from the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) countries and the least developed countries that have signed free trade agreements with Russia will be exempted from tariffs, while imports from developing countries will be subject to tariffs of 75 percent of the basic tariff rate.
According to the latest data released by the WTO, the highest final tariffs on imported products are levied on beverages and tobacco, with an average tariff rate of 23.3 percent. The second category is livestock products, with an average tariff of 23.2 percent. Cotton products to achieve zero tariff. Among the MFN rates committed by Russia, the tariff rate for livestock products is the highest, with an average rate of 25.8%. Next came beverages and tobacco, with an average promised tariff of 22.4 per cent. The cotton goods are promised zero tariff.
Distribution of import tax rates in Russia in 2017
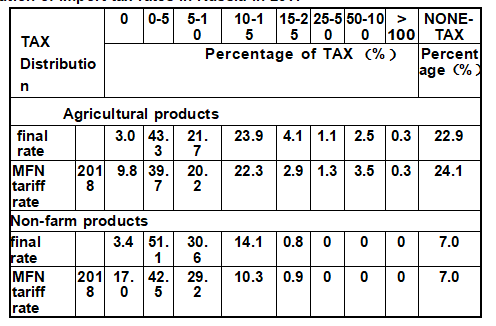
Source: World Trade Organization
Russia's import tax items in 2017 by product classification
[Tariff Quota] Russia imposes quotas on fresh, chilled or frozen meat, including beef (code ТН ВЭД ЕАЭС 0201 or 0202) and some types of poultry (NZ 0207), with separate country-by-country quotas. Quota restrictions on pork (code ТН ВЭД ЕАЭС 0203) have been lifted in favour of a 25 per cent tariff. In addition, since 2013, Russia has imposed quotas on fish scale pine, ginkgo fir, larch and birch logs.
[Export Tariff] The Russian export products basically achieve zero tariff, only a small amount of goods such as natural gas, animal skins, logs, some steel and scrap scrap, aluminum scrap scrap, lead and zinc scrap scrap export tariff.
Russia has started the oil industry tax reform since 2019. The oil export tariff will gradually decrease until it is reduced to zero, while the mining tax rate of mineral resources will be increased accordingly. Based on the average price of crude oil, from April 1, 2020, Russia's oil export tariff will be reduced to $52 / ton. Exports of oil from Russia's eastern Siberian, Caspian and Priazlom fields will remain at zero duty.
From April 1, 2020, the export duty of Russian high-viscosity petroleum will be reduced to $5.20 / ton; Export duties of light petroleum products and lubricants were reduced to US $15.6 / ton, and export duties of heavy petroleum products to US $52 / ton; The export duty of commercial gasoline was reduced to 15.6 USD/ton and that of straight run gasoline (naphtha) to 28.6 USD/ton; Tariffs on petroleum coke fell to $3.30 a tonne; Tariffs on liquefied gas will remain at zero.
- Exhibition Exhibition (Food)
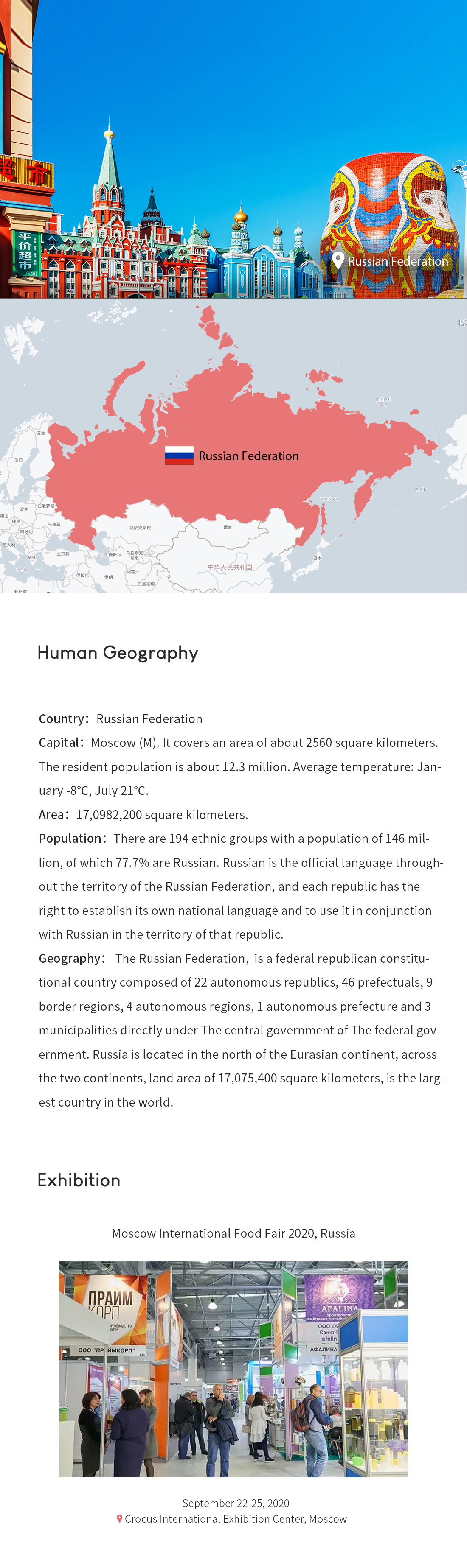
(1) Moscow International Food Fair 2020, Russia
http://www.valuedshow.com/project/food_933.html
The basic information
Name (English) : Moscow International Food Fair 2020, Russia
Name (English) : WorldFood Moscow
Exhibition Date: September 22-25, 2020
Venue: Crocus International Exhibition Center, Moscow
Exhibition cycle: once a year
Organizer: ITE Exhibition Group
Industry attributes
Food and Beverage Fair is a gathering place for buyers of chocolate, candy, baked goods and all kinds of candy
Exhibits range
Integrated foods: cereals, oatmeal, cornflakes, flour, noodles, sugar and starches, spices, salt, condiments, snacks, crisps, crackers, nuts and fruit chips, instant foods (processed)
Frozen food: meat, fish, frozen food, frozen pastries, pies, frozen finished food, frozen fruits and vegetables, frozen and semi-prepared food, canned meat, meat and poultry
Dessert: confectionery, chocolate and cocoa products, fruit products (preserved fruit, jelly), pastry products, gum, honey and jam additives and ingredients, low fat desserts, snacks and snack foods
Packaging and processing equipment: all kinds of food packaging equipment and materials, coffee machine
Beverages: fruit juice and concentrated fruit juice, fruit powder, non-alcoholic drinks, red wine, champagne, beer, liquor and other spirits, loose leaf tea, pressed tea, flavored tea, tea drinks, coffee beans, ground coffee powder instant coffee, coffee drinks
Seafood products: canned fish, live and frozen fish, frozen fish, salted fish, dried fish, smoked fish, salted sturgeon, caviar, preserved fish, semi-processed fish products, seafood
Organic healthy food: food additives, baked goods, sauces and condiments, groceries, oils, fats, sauces, dairy products and dairy products
Fruit and Vegetables: Canned fruits and vegetables, fresh vegetables, fresh fruits and berries, fresh and processed mushrooms
The exhibition to introduce
The annual "Moscow International Food Fair" is an influential exhibition for the food industry in Russia and Eastern Europe. Organized by the famous ITE exhibition group in the UK, the Russian food show has been successfully held for 26 times since its inception in 1992, with the full support of the Russian Ministry of Agriculture and the Moscow municipal government. With the growing prosperity of the Russian food industry, the scale and influence of the exhibition has been increasing year by year, and the number of new halls has been continuously increased.
WorldFood Moscow is the gateway to the Russian food and beverage market. It is the largest food and beverage exhibition in Russia and Eurasian countries. It is the gathering place for buyers of chocolate, candies, baked goods and all candies. Last exhibition scale: more than 200 exhibitors, 6404 visitors, exhibition area of 8552 square meters.
Data of the 2019 Russian Food Exhibition
Last year, 1,764 companies from 64 countries participated in the exhibition, covering an exhibition area of 58,457 square meters. The exhibition attracted a total of 30,768 visitors and buyers from 98 countries.
From 2019, the Moscow Food Show will be held at the Crocus International Exhibition Center. Crocus International Exhibition Center is the largest exhibition center in the Eastern District, with more than 1 million square meters of exhibition space, hosting more than 350 exhibitions and conferences each year. The pavilion is fully equipped with 35,000 free parking Spaces and is close to the MTR station, providing visitors with a higher quality exhibition area and convenience.
The market background
China and Russia have maintained close relations as trading partners for many years. Trade in food and drink between the two countries is also expanding. Russia imports $28 billion worth of food from China each year, and is a major food exporter and a country of 144 million people.
◆ In recent years, with the continuous economic recovery, Russia has become a big consumer in Eastern Europe and its consumption level has been increasing year by year. However, due to its unique geographical environment and climate reasons, food and agricultural and sideline products are scarce, unable to be self-sufficient, and mainly rely on imports. As a big food exporter, China's product quality and price are gradually recognized and supported by Russia and Eastern Europe, and food has become one of the most important products exported to Russia by China.
The export of tea is also worth mentioning. Russia is one of the largest consumers of tea in the world. China is the world's fourth-largest tea exporter, with a 7.8% market share.
◆ Russia Food Fair provides an excellent platform for exhibitors to enter the Russian food industry. We look forward to your participation in Russia's 28 billion USD import market.
(2) food and beverage exhibition in Moscow, Russia WorldFood Moscow at https://www.qufair.com/convention/14218.shtml
Exhibition time: 09.21 ~ 09.24, 2021
Exhibition period: once a year
Exhibition country: Russia
Venue: Moscow, Russia
[Exhibition Introduction]
The exhibition profile
WorldFood Moscow is the most influential exhibition in the food and beverage industry in Russia and Eastern Europe. Organized by the famous British exhibition group HYVE, the exhibition has been successfully held for more than 20 years since its inception in 1992, with the full support of the Russian Ministry of Agriculture and the Moscow Municipal Government.
The exhibition covers all areas of the food industry. For the convenience of exhibitors and visitors, the exhibition is divided into 12 specialized theme areas: Grocery (comprehensive food) area; Frozen food section; Snack food area, canned food area; Edible oil area; Dairy and dairy products section; Meat and Poultry Area; Beverage area; Fish and seafood area; Fruit and vegetable section; Tea and coffee areas; Organic and healthy food section.
Exhibits range
Beverage exhibition area, wine exhibition area, food raw materials exhibition area, canned food exhibition area, meat exhibition area, dairy products exhibition area, fruits and vegetables exhibition area, seafood exhibition area, coffee exhibition area, tea, confectionery, biscuits and snacks, baby food, food processing, packaging technology and equipment, health food, catering services and related technologies.
- Frame section: food categories (list several representative foods)
Bread: A round bread made of buckwheat or wheat flour with eggs and milk. It is the representative food of the Pork Festival.
Soup: a soup made from wild fruits, grass, leaves, etc., or a sweet soup made from fruit or wild fruits.
Vodka: a strong alcoholic drink similar to Chinese liquor.
Lock bread: Bread made of wheat flour with a lock shape and a curved handle. Also called plain white bread.
Bread: A large loaf of wheat flour baked with milk, eggs, and butter. Also called a complete bun.
Gvass: a sour fermented beverage made from rye bread or rye flour mixed with malt; Or frothy drinks made from wild fruit, fruit, or honey.
Scone: a large, long scone filled with meat, fish, cabbage, and rice.
Mead: Liquor made with honey. Cold soup: Cold soup made of kvass, chopped vegetables, meat, etc.
Dumplings: Dumplings made of dough wrapped in meat and boiled in water. They are smaller than Chinese dumplings and are filled mainly with beef.
Pie: to dough bag stuffing baked or fried, but the face of the dead, hair, multi-layer, filling but meat, fish, eggs, cabbage, mushrooms, jam and so on. It is a kind of convenient food often sold on the street and in the market. A fish soup or broth with pickled cucumbers.
Hot water: A hot drink made with honey and spices.
- Brand Recommendation (12 >)
Smino, also known as Crown, mainly produces vodka. Smirnoff is one of the top 10 wines in the world. Smirnoff is one of the best-selling vodkas in the world and is sold in more than 170 countries, making it the number one vodka in the world.
Baltika beer, Lenta retail, Karusel retail.
- Enterprise Recommendation (> 12)
X5 RetailGroup X5 RetailGroup
After a long period of stagnation, X5 Retail Group has steadily increased its Retail revenue. The newly launched «П the "freely" has increased its retail revenue by 25%, with total sales of X5Retail Group reaching 1.29 trillion rubles. X5 Retail Group currently has a market share of 9.4%.
М а f н и т magnet
The past year has been a difficult one for М enlightenment, with a total revenue of 1.14 trillion roubles. On the basis of the positive development of X5 RETAILGROUP, the sales volume of М ideals fell 3.37%. М The ipo is now pioneering new territory and is about to enter the wholesale industry and drugstore sector.
- Professional data
- Country and food data
(1) Analysis report of Russian imported food in the first half of 2018
https://www.tdata.cn/report/content/index/id/267547754.html
- China has become the largest importer of Russian food 11 of the Russian food exports %
http://www.hxnews.com/news/gj/gjxw/201702/04/1153881.shtml(3) Chinese food into Russia's largest importer of https://www.bytop.com.cn/news/zhong guochengeluosishipinzuidajinkouguo.html
(4) the Russian nuts market data analysis https://www.bytop.com.cn/news/zhongguochengeluosishipinzuidajinkouguo.html
imports increased year by year - Oriental wealth
Analysis report of Russian imported food in the first half of 2018
https://www.tdata.cn/report/content/index/id/267547754.html
Chinese Embassy and Consulate General in Russia
Embassy of the Russian Federation
Ambassador: Zhang Hanhui
Address: No.6, UL. Druzhby, Moscow, Russia,117330
No. 6 Friendship Street, Moscow, Russian Federation
Zip code: 115127
Telephone: 0074999518443
Fax: 0074999518321
Website: http://ru.china-embassy.org/chn/ (Chinese)
http://ru.china-embassy.org/rus/ (Russian)
http://ru.chineseembassy.org/chn/ (in Chinese)
http://ru.chineseembassy.org/rus/ (ru)
E-mail: chinaemb_ru@mfa.gov.cn
E-mail: ru@mofcom.gov.cn Chinese website: ru.mofcom.gov.cn
Russian website: ru2.mofcom.gov.cn
Consulate-General in Kazan (Russia)
CONSULATE-GENERAL OF THE PEOPLE'S REPUBLIC OF CHINA IN KAZAN
Consul General: Wu Yingqin
Website: http://kazan.china-consulate.org/chn/
http://kazan.chineseconsulate.org/chn/
Consulate-General in Vladivostok (Russia)
CONSULATE-GENERAL OF THE PEOPLE'S REPUBLIC OF CHINA IN VLADIVOSTOK
Consul General: Yan Wenbin
Telephone: 007-4232-497204, 007-4232-495035
Fax: 007-4232-497459, 007-4232-497210
Website: http://vladivostok.china-consulate.org/chn/
Economic and Commercial Office, Consulate-General of China in Vladivostok
Territory: Primorsky Krai (Vladivostok), Sakhalin (South Sakhalinsk), Magadan (Magadan), Kamchatka Krai (PetroPavlovsk Kamchatka), Chukchi Autonomous Region (Anadyr)
Address: No. 3 Krykin Street, Vladivostok, Primorsky Krai, Russia 690065
Telephone: 007-4232-3016 87
Fax: 007-4232-4974 59
E-mail: knr.konsulstvo@mail.ru
Website: vladivostok.chineseconsulate.org
Consulate General in Irkutsk (Russia)
Consul General: Cao Yunlong
Contact number: 007-3952-781431
Fax number: 007-3952-781438
Postal address: No. 40 Karl Marx Street, Irkutsk, Russia
Zip code: 664007
Website: http://irkutsk.chineseconsulate.org/
E-mail: consulate_irkutsk@mfa.gov.cn
Economic and Commercial Office, Consulate General of China in Irkutsk, Russia
Territory: Irkutsk Prefecture (Irkutsk City), Waibaikal Krai (former Chita Prefecture and Agabriyat Autonomous Region, later Baikal City), Republic of Buryat (Ulan Ude City), Republic of Tuva (Kizil City), Hakasi Republic (Abakan City).
Address: No. 11 Kutnizovo Street, Irkutsk, Russian Federation 664038
Telephone: 007-3952-781432 Fax: 007-3952-781438
E-mail: irkutsk@mofcom.gov.cn Website: irkutsk.mofcom.gov.cn
Consulate-General in Yekaterinburg (Russia)
Consul General: Cui Shaochun
Telephone: 007-922-1509 999
The 007-922-6193 399
Fax: 007-343-2535 784
Website: http://ekaterinburg.chineseconsulate.org
Economic and Commercial Office, Consulate General of China in Yekaterinburg, Russia
Region: sverdrovsk (yekaterinburg), krasnoyarsk krai (krasnoyarsk), Novosibirsk (Novosibirsk), omsk (omsk), tyumin (tyumin), Chelyabinsk (Chelyabinsk).
Address: 45 Tchaikovsky Street, Yekaterinburg, Russian Federation Tel: 007-343-2535782
Fax: 007-343-2535 784
E-mail: ykjlbjss@mofcom.gov.cn
Address: ekaterinburg. Mofcom. Gov. Cn /
Consulate General in Khabarovsk (Russia)
CONSULATE-GENERAL OF THE PEOPLE'S REPUBLIC OF CHINA IN KHABAROVSK
Consul General: Cui Guojie
Address: 680028, Stadium OF Lenn, Khabarovsk, Russia
Zip code: 680028
Country code: 007-4212
Telephone:
Duty: 306163
Laboratory: 302353
Consular Office: 328390
Office: 421601
Economic and Commercial Office: 304561
304621
Fax: 311759
Website: http://www.fmprc.gov.cn/ce/cgkhb/chn/
http://www.chinaconsulate.khb.ru/
E-mail: chinaconsul_khab_ru@mfa.gov.cn
Economic and Commercial Office, Consulate General of China in Khabarovsk, Russia
Territory: Khabarovsk Krai (Khabarovsk City), Amur State (Blagoveshchensk City), Jewish Autonomous Prefecture (Birobizhan City), Sakha (Yakutia Republic).
Address: North Building, Lenin Stadium, Khabarovsk, Russian Federation
Zip code: 680028
Tel: 007-4212-304621 Fax: 007-4212-304561
Email: jskhv@mail.ru. Address: khabarovsk.mofcom.gov.cn
Consulate General in St. Petersburg (Russia)
CONSULATE-GENERAL OF THE PEOPLE'S REPUBLIC OF CHINA IN ST.PETERSBURG
Consul General: Wang Wenli (Female)
No.134, Nab. Kanala Griboedova, St. Petersburg
P.O. Box: Nab. Kanala Griboedova, No. 134, St. Petersburg, 190121, Russia
Zip code: 190121
Website: http://saint-petersburg.china-consulate.org
http://saint-petersburg.chineseconsulate.org
http://stpetersburg.china-consulate.org
http://stpetersburg.chineseconsulate.org
Telephone:
Outside group: 007-812-7146230
Consular Office: 007-812-7137605
Office: 007-812-7138009
Mobile phone on duty: 007-9627035069
Fax: 007-812-7144 958
E-mail: chinaconsul_sp_ru@mfa.gov.cn
Economic and Commercial Office, Consulate General of China in St. Petersburg, Russia
Region: Petersburg City, Leningrad State, Murmansk State (Murmansk City), Novgorod State (Nizhny Novgorod City), Arhangelsk State (Archangelsk City), Pskov State (Pskov City), the Republic of Karelia (Petrozavodsk City).
Address: No. 134 Canal Shore Street, Gryboyedov, St Petersburg, Russia: 190046
Telephone/Fax: 007-812-4951771
E-mail: rsp@mofcom.gov.cn
The Consulate General's telephone number: 007-812-7147670
On duty 24 hours a day: 007-812-9425929
E-mail: chinaconsul_sp_ru@mfa.gov.cn
- Russian Embassy and Consulate in China
Embassy of the Russian Federation in China
Embassy of the Russian Federation
Chancery: 4 Beizhong Street, Dongzhimen, 100600
Chancery: No.4, Dong Zhi Men Bei Zhong Jie
Tel: 65322051 65321381 (switchboard) 65321267 65321991 (Consular Office)
Fax: 65324851 (Embassy) (Consular Office)
E-mail: embassybeijing@mid.ru
Website: www.russia.org.cn
Trade Representation Office: No. 27, Ma Pio Hutong
Telephone: 65324627 65325418
Fax: 65325398
E-mail: info@russchinatrade.ru
Website: www.russchinatrade.ru
Commercial Representative Office of the Russian Federation in China (Beijing)
Add: No. 4, Beizhong Street, Dongzhimen, Beijing 100600
Telephone: 010-65324627, Fax: 010-65325398
Email: info@russchinatrade.ru Website: Email
Consulate General of the Russian Federation in Shenyang
Consulate General of the Russian Federation in Shenyang
Chancery: 31 Nanshisanwei Road, Heping District, Shenyang City, Liaoning Province, China
Chancery: 31Nan Shisanwei Road, Heping District, Shenzhen, Liaoning Province
Tel: 024-23223927
Fax: 024-23223907
Area: Liaoning, Jilin
DISTRICT: Liaoning, Jilin
Consulate General of the Russian Federation in Shenyang District: Liaoning, Jilin, Heilongjiang
Consulate General of the Russian Federation in Guangzhou
Consulate General of the Russian Federation in Guangzhou
Chancery: Unit A, 26 / F, Zhujiang New Town Development Center, No. 3 Linjiang Avenue, Zhujiang New Town, Guangzhou 510623, Guangdong Province
Chancery: 26/A, Development Center, 3 Linjiang Avenue, Zhujiang New City Guangzhou, Guangdong Province
Telephone: 020-85185001/02/03
Fax: 020-85185099 (Office), 85185088 (Visa Section)
Email: gzconsul@hotmail.com, email
Region: Guangdong, Fujian, Hainan, Yunnan, Jiangxi, Guangxi
District: Guangdong, Fujian, Hainan, Yunnan, Jiangxi, Guangdong
Consulate General of the Russian Federation in Shanghai
Consulate General of the Russian Federation in Shanghai
Chancery: 20 Huangpu Road (Building of the Russian Consulate General in Shanghai), Shanghai, 200080
Chancery: 20 Huangpu Road, Shanghai
Tel: 021-63242682
Fax: 021-63069982
Area: Shanghai, Zhejiang, Jiangsu, Anhui
District: Shanghai, Zhejiang, Jiangsu, Anhui
Commercial Representative Office of the Russian Federation in China Shanghai Branch
Tel: 021-63240026 Fax: 021-63240029
E-mail: info@russchinatrade.ru
Tel: 021-63248383, 021-63242682 Fax: 021-63069982
Economic and trade organizations (Chamber of Commerce)
Russia-China General Chamber of Commerce
Basic information of Russia-China General Chamber of Commerce:
Russia China general chamber of commerce was founded in 2006 on April 15, Russian name for "С о ю з К и т а й с seem и х П р е д р и н и м а т е л е й kind guide Р о с с и и" (hereinafter referred to as "С К П"). The current president unit is the European Business Development and Investment Management Center, which has more than 4000 member companies (including individual businesses).
Russia the aim of the Chinese general chamber of commerce and task is to strengthen exchanges and cooperation between Chinese companies across the country, provide members with various kinds of policy information, business consulting and legal services, enhance Chinese enterprises with the Russian government departments and business communication, reflecting the desire and demand of members, safeguard the legitimate rights and interests of members, promoting the development of economic and trade relations between China and Russia.
Since its establishment, the General Chamber of Commerce has established a stable relationship with the relevant federal departments and the Moscow Municipal Government, laying the most important foundation for better protection of the legitimate rights and interests of its members.
With the tenet of communication, liaison, information consultation and emergency assistance, the chamber implements the strategy of sharing internal information resources, strengthening communication among enterprises and expanding the influence of Chinese-funded enterprises, so as to enable its members to better integrate into the social and economic life of Russia, and strive for survival and development.
Chamber of commerce (address: Moscow xincun street, no. 4 (У л и ц а Н о kind guide о с л о б о д с seem а second, д о м 4) chamber of commerce web site: www.cgccru.org/zh/3
Contact person: Fu Yanjie (Secretary General) Tel: 007-495-9953736 Fax: 007-495-7888872
Email address: info@cgccru.org
Russian Investment Service Agency
(1) Union of Russian Industrialists and Entrepreneurs
Russia's most influential enterprise alliance organization, in the whole territory of Russia has thousands of large member enterprises, more than 100 industries and local branches, covering machinery manufacturing, investment, finance, national defense industry, construction, chemical, light industry, food industry, service industry and other important economic fields.
Chairman: Shauhin Alexander Nikolaevich.
Address: No. 17 Katerinicheskaya Yanhe Street, Moscow City, Russian Federation: 109240
Tel: 007-495-6630404 Fax: 007-495-6630432
E-mail: rspp@rspp.ru Website: rspp.ru
(2) Russian Secretariat of China-Russia Chamber of Commerce for Machinery and Electronics. The China-Russia Chamber of Commerce in Mechanical and Electrical Engineering was established at the initiative of the two heads of state. Mr. Zhang Yujing, President of China Chamber of Commerce for Import and Export of Mechanical and Electrical Products, will be the President of the China-Russia Chamber of Commerce for Import and Export of Mechanical and Electrical Products, and Mr. Vekschelberg Viktor Feliksovich, President of the Russian side. The Russian secretariat of the China-Russia Chamber of Commerce for Machinery and Electronics is located in Moscow.
Address: No. 40 Petit Oldenka Street, Moscow, Russian Federation 115184
Tel/Fax: 007-495-7204999 (extension 5096) E-mail: d.prudov@chamber-rc.ru
Website: www.chamber-rc.ru
(3) Russia-China Bilateral Business Council
The China-Russia Bilateral Entrepreneurs Council is an enterprise cooperation mechanism established under the framework of the China-Russia Friendship, Peace and Development Committee Subcommittee on Promoting Enterprise and Industrial Cooperation. Chinese Chairman: Ren Hongbin, Chairman of China National Machinery Industry Corporation. President of Russia: Timchenko Gennady Nikolaevich.
Address: Building 1, No. 7 Geregatskaya Street, Moscow, Russian Federation 127473
Telephone: 007-495-921-7463 Fax: 007-495-649-1821
Email: info@rcbc.ru Website: Email
(4) Industrial Russia
The Russian social organization "Industrial Russia" is an enterprise alliance in the field of non-raw material economy. Chairman: Lepik Alexei Yevgenievich.
Address: Building 1, No. 7 Geregatskaya Street, Moscow, Russian Federation 127473
Tel: 007-495-6491826 Fax: 007-495-6491819
Email: info@deloros.ru Website: Email
(5) Federation of Asian Industrial Entrepreneurs of Russia
Chairman: Monkevich Vitaly Vikentijevic
Address: Building 1, No. 13, No. 1 Kadashevsky Alley, Moscow, Russian Federation, 115035
Tel: 007-495-136-9992
Email: office@raspp.ru Website: China Representative Office (Guangzhou)
Address: Room 601, Hejingruifeng L7, No. 12, Haile Road, Zhujiang New Town, Tianhe District, Guangzhou City, Guangdong Province Tel: 0086-20-38200703
E-mail: china@raspp.ru
 |
 |
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
 |
 |
||
 |
|||||