EFL · National City (Japan)
- national elements
Flag:Japan

Landmark: Tokyo Tower

[Country name] Japan (にほんこく)
[Area] 378,000 square kilometers, including the four large islands of Hokkaido, Honshu, Shikoku and Kyushu and more than 6,800 other small islands.
[Population] Japan's total population is 126 million (March 2021). The main ethnic group is the Yamato, and there are about 16,000 Ainu in Hokkaido. Japanese is spoken, and Ainu is spoken by a small number of people in Hokkaido. The main religions are Shinto and Buddhism, which account for 49.6% and 44.8% of the religious population respectively.
[Capital] Tokyo, population about 13.96 million (December 2020).
Emperor Naruhito, who ascended the throne on May 1, 2019 under the title Reiwa.
The Emperor's birthday: February 23 (equivalent to the National Day). Founding anniversary: February 11 (according to the solar calendar calculated by the 7th century BC, the first generation of the emperor of Japan, Emperor Shenwu New Year's day).
Located on the west coast of the Pacific Ocean, it is an island nation with an arc extending from northeast to southwest. It faces China, North Korea, South Korea and Russia across the East China Sea, Yellow Sea, Korea Strait and Sea of Japan. Is a temperate Marine monsoon climate, mild and humid all the year round. June more plum rain, summer and autumn more typhoons. The average temperature in January is -6°C in the north and 16°C in the south. 17°C in the north and 28°C in the south in July.
Japan is located in the Pacific Ring of Fire, earthquakes, volcanic activities are frequent. One in ten of the world's volcanoes are located in Japan, and one in five earthquakes occur in Japan. The Great Hanshin earthquake in 1995 and the Zhong-Yue earthquake in New encompassed Prefecture in 2004, which caused heavy human and property losses, attracted worldwide attention. On March 11, 2011, Japan was hit by a 9.0 magnitude earthquake, which triggered a tsunami and a nuclear power plant leakage accident, and was called "Japan's worst crisis since the war".
Japan was defeated in World War II and announced its unconditional surrender on August 15, 1945. In the early postwar period, the US military alone occupied Japan. In 1947, the new Constitution was promulgated and implemented, and the country was transformed from a Heavenly Emperor to a parliamentary cabinet system with the Emperor as the national symbol. After the war, it pursued the "emphasis on economy and light on armaments" and became the second largest economic power in the West in the late 1960s. Since the mid-1980s, he has put forward the goal of becoming a major political power. In the 1990s, the economy fell into a long-term downturn. Since 2002, it has experienced a slow recovery, which is the longest on record in the post-war period. Since 2008, China has been hit by the global financial crisis and the massive March 11 earthquake, and its economic recovery has suffered a setback. Since Shinzo Abe took office again at the end of 2012, he has vigorously promoted "Abenomics" and implemented a series of economic stimulus policies, which have boosted Japan's economy to some extent. In 2020, impacted by COVID-19, real GDP showed negative growth for the first time since 2009. Diplomatically, Japan adheres to the Japan-US alliance, attaches importance to multilateral diplomacy and strives to play an important role in international affairs.
[Governance] The legislative, judicial and executive powers are separated. The emperor is a symbol of the state and has no right to participate in state affairs. The Congress is the highest power and the sole legislative body, divided into two houses, the Senate and the House. The Cabinet is the highest administrative organ, responsible to the National Assembly. The Prime Minister (also known as the Minister of the Cabinet) is elected by the National Assembly and appointed by the Emperor.
The LDP currently governs in a coalition with New Komeito. The ruling party has stable majorities in both the House of Representatives and the Senate.
【 Constitution 】 The current Constitution of Japan was promulgated and implemented on May 3, 1947. Article 9 of the Constitution states: "Japan forever renounces the right of the state to wage war, the threat or exercise of force as a means of settling international disputes. To this end, Japan does not maintain land, sea, air and other war forces, nor does it recognize the belligerent right of the state." This has become an important guarantee for Japan to follow the path of peaceful development after the war, and also an important guarantee for Japan to be a peaceful country.
【 Congress 】 is composed of the House of Representatives and the Senate, the highest authority and the sole legislature. The House of Representatives is elected to 465 four-year terms. The Prime Minister has the power to dissolve the House of Representatives and call a general election. The Senate has 245 members. Senators serve six-year terms, with half elected every three years and cannot be dissolved. The House of Representatives is superior to the Senate in power. The General Assembly meets from January to June each year for 150 days. At other times provisional and special parliaments may be convened as necessary. Oshima Tadamori, the current speaker of the lower house, took office in April 2015. Senate Speaker Santo Akiko, since August 2019.
The Cabinet is the highest executive, responsible to the Congress. It consists of the Prime Minister (Prime Minister) and ministers in charge of the provincial offices. The Prime Minister of the Cabinet is nominated by the National Assembly and appointed by the Emperor. Other Cabinet members are appointed and removed by the Prime Minister of the Cabinet and verified by the Emperor. Japan's administrative agency is responsible for the national administrative affairs in the Japanese government agencies, mainly is the cabinet of the various government agencies, generally refers to the state administrative organic law, "the administrative organ of the state" provisions of the province and outside the office (committee, the office), and specified in the act of the cabinet office set up outside of the cabinet office and bureau (committee, the office). The Cabinet Office is an administrative organ at a higher level than the provinces in order to strengthen the functions of the Cabinet. Relative to local public organizations (local governments), it is called the Central Government Office, the Central Provincial Government (Central Government), or the Provincial Office for short.
[Administrative Districts] There are 47 first-level administrative districts in Japan, which are divided into 1 capital (Tokyo), 1 prefecture (Hokkaido), 2 prefectures (Osaka Prefecture and Kyindu Prefecture) and 43 prefectures. The capitals, prefectures, prefectures and counties are parallel, first-level administrative regions directly under the central government, but each of them has autonomy, and the local chief executives and parliaments are elected by the local voters.
Judicial power is vested in the Supreme Court and its subordinate courts. Adopt "four level three examination system". The Supreme Court is the court of final appeal and hears constitutional and other major cases. The High Court is responsible for the second instance, and there are eight courts nationwide. Each capital, prefecture, prefectural and prefectural courts have one (four in Hokkaido), responsible for the first instance. There are also summary courts and family courts throughout the country which are responsible for civil and criminal proceedings not exceeding fines. The Chief Justice (President) of the Supreme Court is nominated by the cabinet and appointed by the emperor. The 14 justices are appointed by the cabinet and are subject to a national vote. Judges at other levels are nominated by the Supreme Court and appointed by the Cabinet to 10-year, renewable terms. A judge at any level may not be removed from office without formal impeachment. The current Supreme Court chief, Otani Naoto, took office in January 2018.
Corresponding to the four levels of courts, procuratorial organs are divided into the highest procuratorial office, the higher procuratorial office, the local procuratorial office and the district (town) procuratorial office. Public procurators are divided into chief procurators (chief procurators), deputy procurators (chief procurators), chief procurators (chief procurators of higher levels), procurators (chief procurators of local areas), deputy procurators, etc. Officials above the Attorney General are appointed by the Cabinet. The Minister of Justice has command over the Attorney General. Current Attorney General Hayashi Makoto has been in office since July 2020.
[Economy] Japan is the third largest economy in the world, with a nominal GDP of 551.1 trillion yen in 2020 and a real growth rate of -4.8%. By the end of April 2020, China's foreign exchange reserves had reached US $1,368.5 trillion. Exchange rate: 1 USD ≈107 Yen (May 2020). Total unemployment rate: 2.9 percent (March 2021). The main industries are automobile industry, animation industry, digital media industry, erotic industry, electronic manufacturing liquid, fishing, shipping industry.
Japan's GDP and growth rate from 2015 to 2019
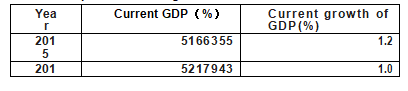
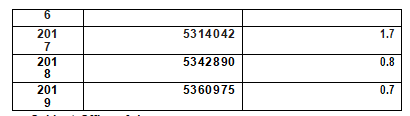
Source: Cabinet Office of Japan
Major economic figures for 2019 are as follows:
GDP: US $508 million
GDP growth rate: 0.7%
GDP per capita: US $40,000
Currency name: Japanese yen
Inflation rate: 0.6% (2020)
Unemployment rate: 2.4 percent
Public debt: 1,114.54 trillion yen, or 238 percent of GDP
Deficit to GDP: 2.1%
[Resources] Lack of resources, more than 90% of the country is dependent on imports, of which petroleum is completely dependent on imports. The Japanese government actively develops nuclear energy and other new energy sources. By February 2011, Japan had 54 nuclear power units with a total installed generating capacity of 49.467 million kilowatts, ranking the third in the world. After the nuclear leakage accident of Fukushima nuclear power plant in March 2011, four reactors of Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant were declared invalid, and all nuclear power plants in Japan were shut down. In July 2012, units 3 and 4 of the Kansai Electric Power Company's Oi nuclear power plant in central Japan were temporarily restarted in response to power shortages, but were shut down again in September 2013 for regular inspections. In August 2015, Japan restarted the No. 1 reactor at the Kawauchi Nuclear Power Plant in Kagoshima Prefecture after a two-year hiatus, and in October, it restarted the No. 2 reactor at the Kawauchi Nuclear Power Plant.
The forest area of Japan is about 25.08 million hectares, accounting for nearly 2/3 of the total land area, and the forest coverage rate is about 67%, which is one of the countries with the highest forest coverage rate in the world. The self-sufficiency rate of wood is only about 20%, and it is the country that imports the most wood in the world. Japan has many mountains and rivers, rich in water resources, and about 135.3 billion kilowatt hours of reserves per year. Japan's exclusive economic zone is about 10 times the size of the country and is rich in fish.
Japan is one of the largest industrial countries in the world. Japan's heavy industry includes metal industry, machinery industry, chemical industry; Light industry includes textile industry, food industry, pharmaceutical industry, paper and pulp industry and other industries. In 1997, machinery industry accounted for 44.7 percent of total industrial production, metals 12.4 percent, food 10.9 percent, chemicals 10.3 percent, textiles 2.8 percent and other 18.9 percent.
[Agriculture and Animal Husbandry] Leisure agriculture is the main mode of agricultural development in Japan, which mainly includes citizen farm, sightseeing farm, homestay farm, agricultural park and forest park. Among them, sightseeing farm is also very common in China, which is one of the main modes of the development of agriculture in China. In Japan, the more popular sightseeing farm has Aomori apple experimental farm and cherry production garden, as well as the "Oriental Provence" said Japan Hokkaido Fuyano Futien Farm, the farm focuses on the development of lavender sightseeing park.
[Foreign Trade] Foreign trade plays a very important role in Japan's economy. According to the statistics of Japan's Ministry of Finance and JETRO, in 2019, the import and export of Japan's goods trade reached $1.43 trillion, a year-on-year decrease of 4.0%. Among them, the export was US $705.68 billion, down by 4.4% year on year; Imports reached US $720.76 billion, down 11.5 percent year on year. The trade deficit was $15.08 billion.
[Major Trade Partners] According to the statistics of Japan's Ministry of Finance and JETRO, the Chinese mainland, the United States and the Republic of Korea are Japan's top three trading partners in 2019, with bilateral trade volume of US $303.95 billion, US $219.09 billion and US $75.82 billion respectively.
Transportation equipment, mechanical equipment and mechanical and electrical products are the main exports of Japan. In 2019, the exports amounted to US $166.17 billion, US $138.65 billion and US $121.20 billion, accounting for 23.5 percent, 19.6 percent and 17.2 percent of Japan's total exports. Fossil fuels, mechanical and electrical products and chemical products are the top three categories of imported goods in Japan, which accounted for US $155.37 billion, US $109.99 billion and US $74.86 billion in 2019, accounting for 21.6 percent, 15.3 percent and 10.4 percent of Japan's total imports.
- Japan's trade in goods
- Amount of import and export of goods
According to Japanese customs statistics, the value of Japan's imports and exports of goods in 2018 was $1,466.57 billion. In 2019, Japan's imports and exports of goods were US $1,426.27 billion, down by 4.1% compared with the previous year (the same below).
Trends of Japan's imports and exports of goods and their growth rates from 2015 to 2019
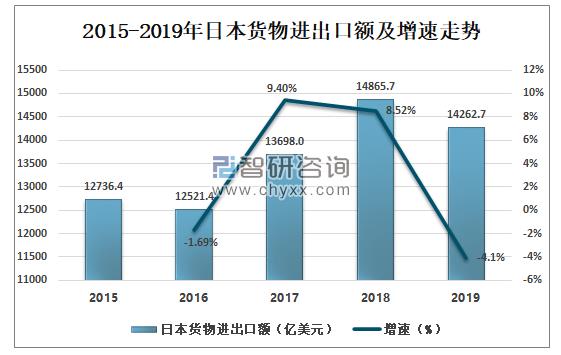
Among them, the export of goods from Japan was US $705.53 billion, down 4.4%; Japan's imports of goods were $720.74 billion, down 3.7 percent. The trade deficit was US $15.21 billion.
Total value of imports and exports of Japanese goods from 2015 to 2019

Data source: Japan Customs, Zhiken Consulting
- Major trading partners of Japan
In terms of countries (regions), the United States, China and the ROK are Japan's top three export trading partners. In 2019, Japan's exports to the United States reached US $139.80 billion, down 0.2% and accounting for 19.8% of Japan's total exports.
The amount and proportion of Japan's exports to the United States from 2015 to 2019
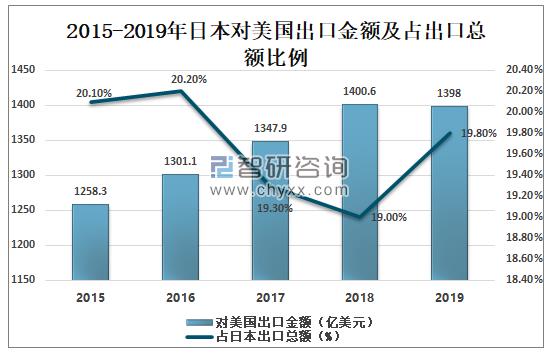
Data source: Japan Customs, Zhiken Consulting
Data released by IPRS shows that in 2019, Japan's export to China reached 134.69 billion US dollars, down 6.4%, accounting for 19.1% of Japan's total export.
Amount and Proportion of Japan's Exports to China from 2015 to 2019
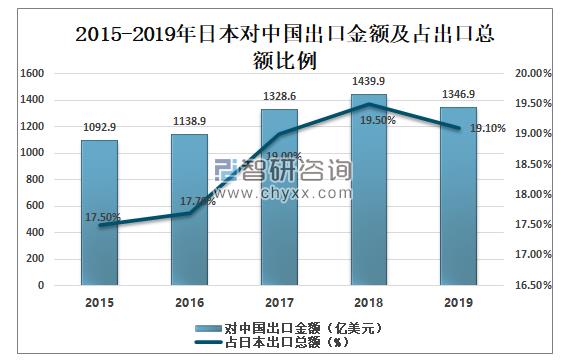
Data source: Japan Customs, Zhiken Consulting
In 2018, the value of Japan's exports to South Korea was US $52.51 billion, and in 2019, the value of Japan's exports to South Korea was US $46.25 billion, down 11.9%, accounting for 6.6% of Japan's total exports.
The amount and proportion of Japan's exports to South Korea from 2015 to 2019
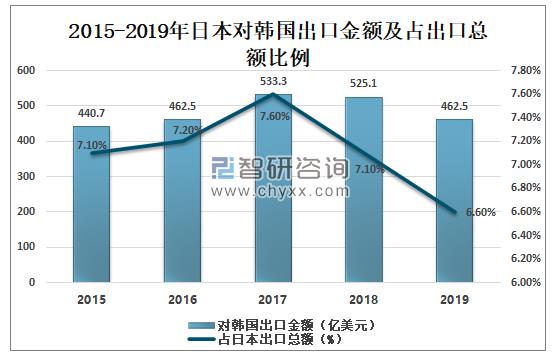
Data source: Japan Customs, Zhiken Consulting
In 2019, Japan's imports from China reached US $169.22 billion, down 2.5% and accounting for 23.5 percent of Japan's total imports.
Amount of Japan's Imports to China and Its Proportion in Total Imports from 2015 to 2019
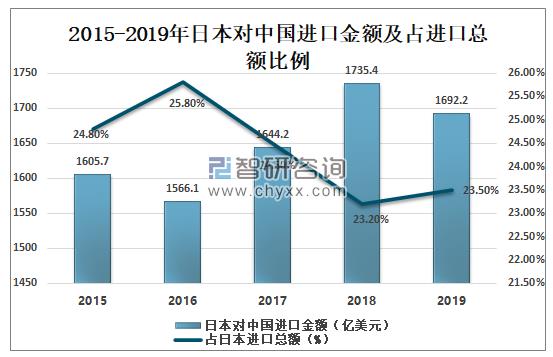
Data source: Japan Customs, Zhiken Consulting
In 2018, Japan's imports from the US totaled US $81.55 billion, and in 2019, Japan's imports from the US totaled US $79.08 billion, down 3.1 percent and accounting for 11 percent of Japan's total imports.
Amount of Japan's Imports to the US and Its Proportion in Total Imports from 2015 to 2019
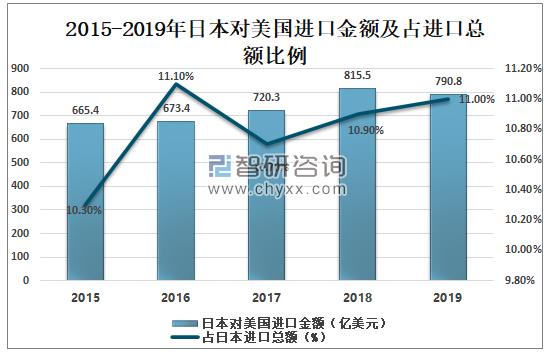
Data source: Japan Customs, Zhiken Consulting
In 2018, Japan's imports from Australia were 45.69 billion US dollars, and in 2019, Japan's imports from Australia were 45.45 billion US dollars, down 0.6%, accounting for 6.3% of Japan's total imports.
Amount of Japanese Imports to Australia and Its Proportion in Total Imports from 2015 to 2019

Data source: Japan Customs, Zhiken Consulting
The major sources of Japan's trade deficit in 2019 are China, Australia and oil producers in the Middle East. The US, Hong Kong and the Republic of Korea are the top three sources of trade surplus for Japan, with surpluses of US $60.72 billion, US $31.56 billion and US $16.64 billion respectively in 2019.
3, Japan's main import and export trade commodities
Mechanical and electrical products, transportation equipment and chemical products are Japan's major exports. In 2019, the value of Japan's exports was US $240.050 billion, US $167.84 billion and US $61.55 billion. Mechanical and electrical products and transportation equipment decreased by 6.7% and 2.8% respectively, while chemical products increased by 0.8%. They accounted for 34.0%, 23.8% and 8.7% of Japan's total exports.
Japan's Top 3 Commodity Exports, 2015-2019 ($100 million)

Data source: Japan Customs, Zhiken Consulting
Among them, China is the largest exporter of mechanical and electrical products. In 2019, Japan's mechanical and electrical products exported to China amounted to 54,875 million US dollars, accounting for 22.9% of Japan's total mechanical and electrical products exports. The United States is the second largest, accounting for 19.6 percent of Japan's total electromechanical products, at $46,933 million.
Amount and proportion of Japan's mechanical and electrical products exports to major countries in 2019
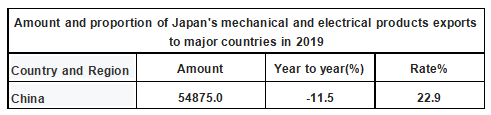
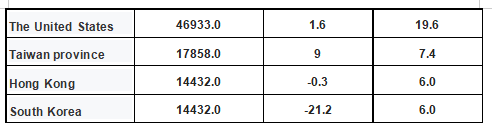
Data source: Japan Customs, Zhiken Consulting
In 2019, the main export country of transportation equipment, the United States, was 52,686 million US dollars, accounting for 31.4% of the total transportation equipment. China was second with $13,820 million, or 8.2 percent.
Amount and proportion of Japan's transportation equipment exports to major countries in 2019
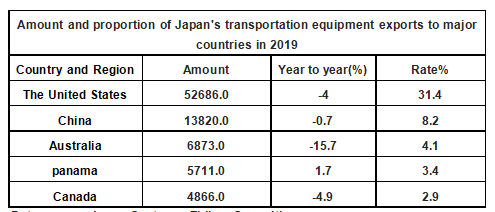
Data source: Japan Customs, Zhiken Consulting
In 2019, the main export country of Japanese chemical products is China, which is 16,889 million US dollars, accounting for 27.4% of the total value of chemical products. The United States followed by 8,850 million dollars, accounting for 14.4 percent of the total value of chemical products.
Amount and proportion of Japan's chemical exports to major countries in 2019
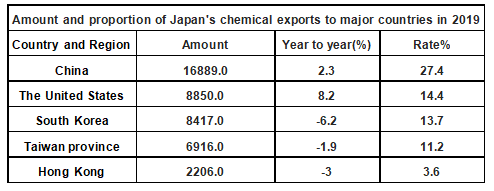
Data source: Japan Customs, Zhiken Consulting
Minerals, mechanical and electrical products and chemical products are the top three categories of imports from Japan in 2019. The import volume in 2019 was US $179.04 billion, US $169.27 billion and US $64.98 billion, down by 9.7%, 2.7% and 3.0%, accounting for 24.8%, 23.5% and 9.0% of Japan's total imports.
Top 3 Imports of Japan from 2015 to 2019 ($100 million)
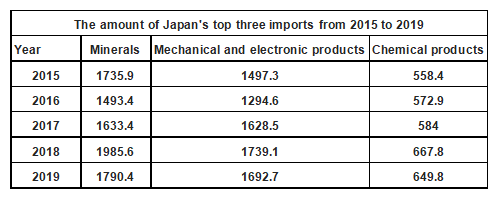
Top 3 Imports of Japan from 2015 to 2019 ($100 million)
Data source: Japan Customs, Zhiken Consulting
Japan's three categories of imported goods are composed of countries/regions, among which China is the main source of mechanical and electrical products. The amount of mechanical and electrical products imported by Japan from China is 78,109 million US dollars, accounting for 46.1% of Japan's total import amount of mechanical and electrical products.
Amount and Proportion of Mechanical and Electrical Products Imports by Major Countries/Regions in 2019 (millions of US dollars)
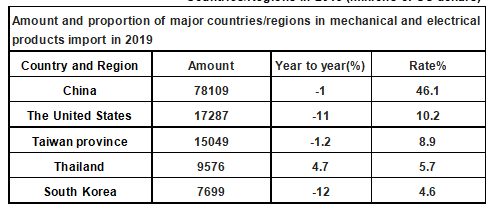
Data source: Japan Customs, Zhiken Consulting
The main source of Japanese mineral imports is Australia, which is 38,363 million US dollars, accounting for 21.4% of the total mineral imports. Next came salad Arabia, which accounted for $26,743 million, or 14.9 percent of the total mineral value.
Amount and Proportion of Mineral Imports by Major Countries/Regions in 2019 (millions of US dollars)
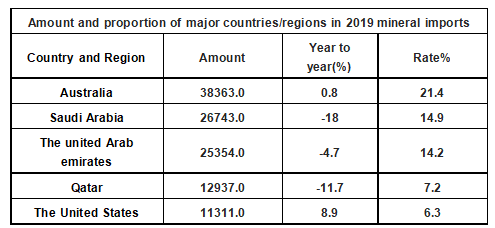
Data source: Japan Customs, Zhiken Consulting
In 1952, China and Japan officially signed the first non-government trade agreement. In 1962, the Memorandum on the Development of Non-government Trade between China and Japan was signed. In 1978, the China-Japan Long-term Trade Agreement was signed. After years of efforts, bilateral economic and trade relations have made considerable progress. As bilateral trade is highly complementary, the two sides have become each other's important trading partners. According to Chinese customs statistics, bilateral trade volume in 2019 was US $315.03 billion, down 3.9 percent year on year. Among them, China's exports to Japan were US $143.27 billion, down 2.6% year on year. Imports from Japan amounted to US $171.76 billion, down 4.9% year on year, leaving China with a deficit of US $28.49 billion. Ranked by region, Japan is China's fourth largest trading partner; Ranked by country, Japan is China's second largest trade target. Japan is a major trading partner of China. Up to 2003, Japan has been China's largest trading partner for 11 consecutive years, and is now China's fourth largest trading partner (after ASEAN, the European Union and the United States). According to Japanese statistics, China has been Japan's largest trading partner since 2007.
China-Japan trade development from 2015 to 2019
(Unit: 100 million US dollars, %)
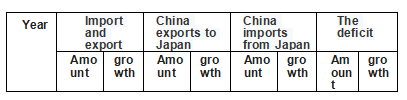

Source: China Customs
In 2020, China-Japan trade totaled US $317.53 billion, of which China exported US $142.66 billion and imported US $174.87 billion.
Japan's top 500 companies in 2020
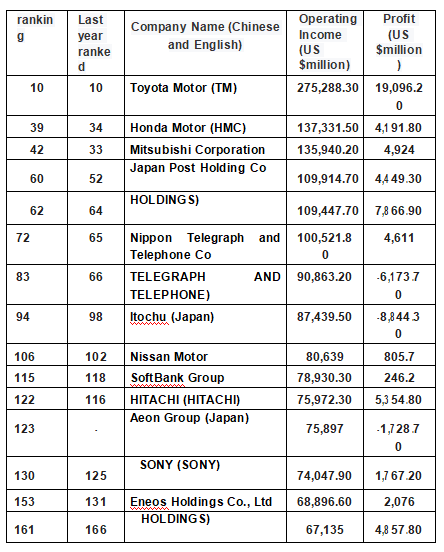
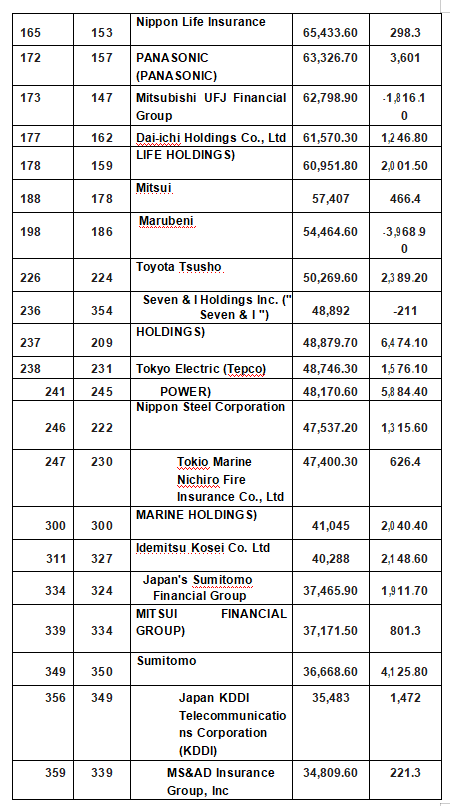
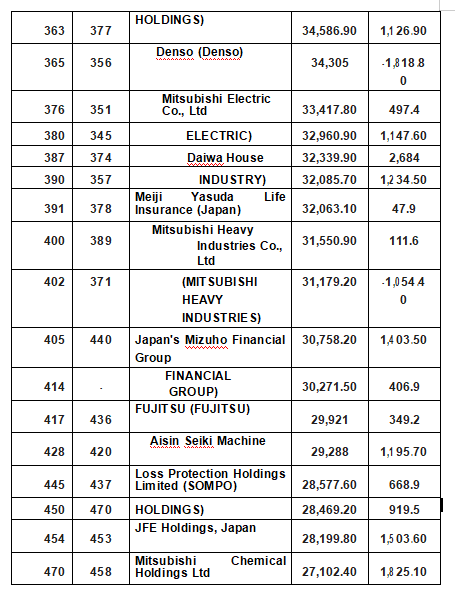
Source: Fortune magazine
Literature and Art
Japan's unique geographical conditions and a long history, gave birth to a unique style of Japanese culture, cherry blossom, kimono, haiku and samurai, sake, Shinto constitute the two aspects of traditional Japan -- chrysanthemum and sword, in Japan has the famous "three ways", namely the Japanese folk tea ceremony, flower way, book way.
The tea ceremony
Also called tea (pin Ming will), since the ancient times as an aesthetic ceremonies by the upper class very love, now, the tea ceremony is used as a training focus, or used for training etiquette and behavior, widely accepted by common people, in Japan there are many teach the tea ceremony of various genres techniques school, many hotels Also has tea room, You can easily enjoy the performance of the tea ceremony.
flowers
As a kind of tea reproduce the techniques of wild flowers in the room, because of display rules and methods are different, the flowers can be divided into more than 20 schools, in Japan there are many teach the flowers of various genres techniques school, in addition, in the great hall of the hotel, department stores, public facilities and other places, enjoy the decoration beautiful flower art.
sumo
Originated from Japanese Shinto religious rituals. People in the game held in the temple to the god of harvest, hope can bring good harvest, in the period of nara and peace, sumo wrestling is a palace to watch sports, and by the kamakura during the warring states period, sumo to become a part of a samurai training, the 18th century is emerging professional sumo, it with the present sumo wrestling, Shinto ceremony emphasizes the sumo, The ritual foot stomping (looking around) before a game is intended to drive away evil spirits from the field, as well as to relax muscles. Salt is also sprinkled on the arena to purify it, because Shinto believes that salt can drive away spirits. Sumo wrestles are held on a platform with a diameter of 4.55 meters and a square platform with a circle in the middle. During the competition, two wrestlers tie their hair in a bun and tie a belt around their lower bodies, nearly naked on stage. Game, its any part besides the soles of your feet shall not touch the surface of the table, at the same time, it shall not exceed the circle, in one minute or even a few seconds can be won or lost, the referee of sumo is made up of 6 people, the referee by hand-held fan "division" stage, the remaining 5 people respectively, east, west, and the referee on the front seat, The highest rank of hercules is yokozungang. The following are Da Guan, Guan Wei, Xiao Jie, and Front Neck. These four grades are called "Mu Nei", which belong to the upper part of Li Tu, and the next one is "Twelve" and "Mu Xiaoxiao". In addition, there are three lower orders, and the third order. The lowest level is called Xikou, and it takes a lot of effort for an ordinary strongman to achieve a higher level. It is impossible to attain the lowest grade without hard work.
The kimono
It is the name of the traditional Japanese national costume. Also known as "Zogo" in Japan, the kimono was made after the Sui and Tang styles of China. The eight to nine century, Japan once popular "tang" clothing, although have change after the formation of Japan's unique style, but it still contains some features of Chinese ancient clothing, women's kimono style and design and color difference is the difference between a sign of age, and married or not, for example, unmarried girls wear tight sleeve outer clothing, married women wear wide sleeve outer clothing; Comb the "Shimada" hairstyle. One of the Japanese hairstyles, a bowl shape > Red collared shirts are for girls and hair is done up in a bun. Plain colored shirts are for matronly women and kimonos with no buttons and only a knotted belt. There are many kinds of belt, and the knot method is also different. A more widely used knot method is called "too drum knot". There is a paper or cloth core in the belt at the back of the waist knot, which looks like a square box. This is what we often see behind the kimono decoration, because the knot is very bother, again after the war have ready-made knot "improvement" and "culture", although today the Japanese daily clothing has been replaced by a suit, but in traditional wedding, celebration, flowers, tea and other grand social occasions, kimono is still recognized will wear the dress.
judo
It has a wide reputation around the world. The basic principle of judo is not to attack, but to use the strength of the opponent to protect the body. The rank of judo is indicated by the color of the belt (elementary: white/advanced: black).
kendo
Derived from the important martial art of samurai swordsmanship, Japanese fencing is a sport in which competitors, wearing special protective gear, stab each other in the head, body, and fingertips with a bamboo knife according to strict rules.
karate
It was introduced to Japan from China through the Ryukyu Kingdom (now Okinawa). Karate does not use any weapons, but only fists and feet. Compared with other fighting sports, it is a form of combat sport with practical significance.
aikido
Originally a sport for practicing "form," the basic idea is to fight against strength without force. Compared to sports such as judo and karate, aikido, without a sense of rudeness, is popular among older people and women as a spiritual exercise and fitness exercise.
Noh, a traditional Japanese drama
Can is a traditional Japanese drama, is also one of the world's oldest living drama, can be originated from the ancient dance drama form and 12 or 13 centuries shrines and temples in Japan held various festival drama, the meaning of "can" have talent or skill, actor through facial expressions and body movements suggest that the essence of the story, not show it. Now this kind of drama still has indomitable vitality in Japan.
- Frame section: hot news
Tokyo International Food Processing and Automation Technology Exhibition (Online)
https://www.showguide.cn/zhanhui/foodtechjapanonline.html
Tokyo International Food Industry Exhibition, Japan
www.showguide.cn
Japanese media: Japanese companies on the "One Belt And One Road" China-Europe Railway
https://baijiahao.baidu.com/s?id=1594679641548846203&wfr=spider&for=pc
Food Hygiene Law of Japan
http://www.cst-test.com/pd.jsp?id=37
- Frame: Country · Human Geography
Japan is an archipelago country in the Pacific Ocean east of Asia. It faces China, Korea and Russia across the East China Sea, Yellow Sea, Korea Strait and Sea of Japan to the west, and faces the Pacific Ocean to the east. The territory consists of four large islands -- Honshu, Hokkaido, Kyushu and Shikoku -- and more than 3,900 smaller ones, covering an area of 377,000 square kilometers. Honshu is Japan's most important island, with an area of more than 227,400 square kilometers, accounting for about 60% of the country's total area. The coastline is nearly 30,000 kilometers long. It is about 3,000 kilometers long from north to south, with mountains running through the center of the archipelago and short, fast-flowing rivers flowing into the surrounding sea. Mountainous and hilly areas account for about 70% of the total territory, and the population is concentrated in limited areas such as rivers and coastal flatlands. More volcanoes, more earthquakes. With more mountains and less land, Japan's tunneling, farming and irrigation techniques improved. There are a total of about 80 volcanoes in Japan, the highest peak of Mount Fuji (3776 meters) is also a volcano, administrative region has 47 prefectures, below the city district Machimura.
Natural Environment in Japan
As a result of the fold and fault action is intense, coupled with the external force action of long-term erosion cutting, the terrain is very broken, the coast twists and turns more harbor. Mountainous areas account for about 76 percent of the country's area. Hokkaido and northern Honshu mountains for the north and south, Shikoku and southern Honshu mountains into the east and west, the two meet in central Honshu, known as the "central mountain knot", for the highest terrain in the country, which has the famous Mount Fuji.
Mount Fuji is an active volcano with an elevation of 3,776 meters and the highest peak in the country. The most recent eruption of Mount Fuji occurred in 1707, and it is still erupting. The mountain is a standard conical shape, with year-round snow on the top, hot springs, waterfalls, and five Fuji lakes in the north. The scenery is beautiful, and the Japanese call it "sacred yue".
Plains account for only 24% of the country's area, mostly scattered in the lower reaches of major rivers and coastal areas. The largest and most famous plain in the country is the Kanto Plain near Tokyo, with an area of 15,770 square kilometers; Next is the Nagoya near the Nono Plain, Osaka, Kyoto near the Kinei Plain and so on. Japan is located in the west coast of the Pacific volcanic seismic belt, is a country with more than 200 volcanoes, including active volcanoes accounted for 1/3. Earthquakes occur frequently, with an average of about four times a day across the country, making it known as the "Earthquake Country". The Great Kanto Earthquake of September 1, 1923 destroyed 73 percent of the houses in Tokyo and 96 percent of the houses in Yokohama, killing 150, 000 people. And volcanic activity is related to the hot springs throughout the country, a total of about 1,200 hot springs. The river is short, full of water, rapids, rich in water resources, but unfavorable navigation. Among them, Shinonugawa is the longest with a length of 367 kilometers; Ligengchuan basin area is the largest, 16,840 square kilometers. There are many lakes, but most of them are small and deep crater lakes, which are distributed in the high mountains, and there are many small lagoons on the coast. The largest lake in China, Lake Pipa, is a structural lake with an area of 686 square kilometers. The surface of the lake is 85 meters above sea level and the deepest is 103 meters.
Japanese islands around the sea, in addition to the northeast coast, are from the tropical Pacific warm current (Kuroshio) around, the climate is regulated by the ocean, the formation of a relatively mild and humid Marine monsoon climate, temperate than the continental latitude area, the precipitation is also richer, the annual average precipitation in most areas for 1000-2000 mm. The prevailing southeast wind in summer, the east coast from June to July rainy continuous; In winter, the northwest wind blows from the mainland through the Sea of Japan. The weather is cold and snowy in the north. Japan extends about 2,400 kilometers from north to south, and its climate varies greatly. It is a monsoon subtropical forest climate south of 35 degrees north latitude. Northern Honshu and Hokkaido are monsoon temperate coniferous forest climate; The rest of the vast area is a monsoon temperate broad-leaved forest climate. Located in central Tokyo, the coldest month (January) average temperature of 6 degrees Celsius, the hottest month (August) average temperature of 25 degrees Celsius, the annual average precipitation of more than 1,500 millimeters. Kagoshima, in the south of Kyushu, has an average temperature of 7 degrees Celsius in the coldest month (L month) and 27 degrees Celsius in the hottest month (August month), with an average annual precipitation of more than 2000 millimeters. In Sapporo, Hokkaido, the average temperature in the coldest month (L) is below -6 degrees Celsius, and the average temperature in the hottest month (August) is above 20 degrees Celsius. The average annual precipitation in the root chamber is 981 mm. Typhoons often hit western and southern Japan between August and October each year, often causing damage.
The Japanese climate
There are four distinct seasons in spring, summer, autumn and winter, with rainfall throughout the year, especially in early summer and autumn. Most of Japan's working areas belong to the temperate zone, suitable for rice cultivation. Due to the narrow territory and the long north-south extension, the climate of the north and south is completely different. The characteristics of the four seasons spring - trees and flowers begin to put on new clothes at the same time. When the cherry blossoms are in full bloom. People really feel the arrival of spring. Summer - Due to the influence of high pressure over the South China Sea, there are more sunny and muggy days. The typhoon formed off the coast of the Philippines between July and October, and the resulting storms caused considerable damage across Japan. Autumn - Leaves begin to change from green to red and yellow. Winter - seasonal winds blow from the north, resulting in continued heavy snow in the sea of Japan and continued dry and sunny weather in the Pacific.
(1) Introduction to Japanese culture - Youku videos
https://v.youku.com/v_show/id_XMjE1MDc2NjAw.html
(2) Creative introduction to Japanese culture -- Youku videos
https://v.youku.com/v_show/id_XMzI1NzA2MzE2MA==
(3) Charming Japan - People's Daily Online
http://travel.people.com.cn/GB/139035/226871/
(4) View of Japan - Bilibili video
https://www.bilibili.com/video/av46623476
- Frame section: the latest information
(1) Research on food safety regulation in Japan
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10183-2010107547.htm
(2) Evaluation and analysis of food safety regulation and governance in Japan -- based on the theory of multi-center governance
http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDRJ201603003.htm
(3) Japan's nuclear waste water discharged into the sea, our food safety is still guaranteed?
https://baijiahao.baidu.com/s?id=1697100135826352898&wfr=spider&for=pc
(4) Food safety in Japan
http://www.banyuetan.org/gj/detail/20201113/1000200033136201605231639695755615_1.html
(5) make trouble or worry! ? South Korea announces bring food to Tokyo Olympics! What is Japan's "food safety problem"?
https://www.sohu.com/a/334049576_173298
(6) The President of the International Olympic Committee expressed his willingness to introduce Japanese food safety
https://www.sohu.com/a/343089458_505479
(7) How does Japan strictly control food safety? What is the cost of food safety "mistakes" in Japan?
https://www.163.com/dy/article/DQMRRSGS05149FK0.html
(8) Yuanqingtian has achieved brilliant achievements in building a bridge of food safety between China and Japan in the past 15 years
https://www.sohu.com/a/357810658_157309
(9) The Global Food Safety Initiative is key to achieving Japan's food safety goals for 2020 and beyond
https://www.prnasia.com/story/189519-1.shtml
(10) The Japanese government invited Chinese media to interview the disaster areas in Fukushima and other places to emphasize food safety
https://www.guancha.cn/internation/2018_11_19_480276.shtml
Two, professional frame section
- Frame section: introduction of country and food
- Frame section: food standards
(1) For the first time, Japan's Ministry of Education issued a decree stipulating the food safety value
https://world.huanqiu.com/article/9CaKrnJtkRO
(2) New development and enlightenment of Japanese food safety supervision system in the 21st century
https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBFX201606012.htm
(3) Japanese Food Safety Law
http://law.foodmate.net/show-168821.html
(4) Basic Law of Food Safety in Japan
http://law.foodmate.net/show-172310.html
(5) quarantine of import and export commodities
Japan has established an inspection and quarantine system for imported food in accordance with the Food Safety Law. Japan's inspection and quarantine of imported food mainly includes: monitoring inspection, ordered inspection and autonomous inspection. The main contents include pesticide residues, toxic and harmful substances, microbial pollution, antimicrobial substances, heavy metal pollution, sulfur dioxide, myeltoxin, standard of materials used, container packaging, anti-decay, anti-deterioration, anti-mildew measures, whether there is a health certificate, preservation standards, etc.
- Framework: Policies and regulations
7.1 Regulations and policies on foreign trade
7.1.1 Trade authorities
The government department in charge of trade in Japan is the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry, whose main responsibility is to comprehensively manage various economic and industrial sectors in Japan, formulate a series of policies and guidelines related to trade and commerce, and strengthen international economic cooperation and exchanges.
7.1.2 Trade legal system
The main trade-related laws in Japan are Tariff Law, Tariff Rating Law, Foreign Exchange and Foreign Trade Law, Trade Insurance Law, Import and Export Transaction Law, Law on the Protection of Dangerous Species of Wild Animals, Law on the Issue of Specific Certificates of Origin of Economic Cooperation Agreements,
Commercial Law, Company Law, Business Registration Law, Financial Commodity Exchange Law, Anti-monopoly Law, Prevention of Unfair Competition Law, Subcontracting Law, Banking Law, Insurance Law,
"Environmental basic law", "law on prevention and control of atmospheric pollution, the act of preventing water pollution, the waste disposal act, the labor standards act, the act of men's and women's employment equality of opportunity," labor health safety ", "the act of sending laborers, the public welfare whistleblower protection act, the administrative organ of personal information protection act," the basic law of intellectual property rights ", "consumer product safety of life Law, etc.
7.1.3 Relevant provisions on trade management
In the 1950s, Japan established the policy of building a nation through trade. In 1955, Japan joined the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT), and in 1958, it abolished trade import control.
[Import Administration] Commodities that are absolutely prohibited to be imported from Japan: counterfeits of currency, paper money and negotiable securities; Indecent books, pictures and carvings; Child pornography; Articles that infringe upon the right of trademark, copyright, copyright, design, etc.; The articles constituting an unfair act specifically referred to by the Law on the Prevention of Unfair Competition; Specific pathogens; Cannabis, opium and other drugs and smoking supplies, guns and ammunition, explosives, gunpowder, chemical weapons and specific substances specified by the relevant laws, etc.
Imports subject to the quota system: according to article 4, paragraph 1, of the Import Trade Administration Order, imports subject to the quota system of Japan include herring, cod and small cod and their roe; Small dried fish, fish š• fish, sardines, mackerel, mackerel, scallop, scallop, dried squid, edible seaweed (seaweed, kelp) and seaweed seasoning and other aquatic products and nuclear fuel
According to the tariff act, the tariff rate method, etc., to milk, butter, dried beans, feed corn, peanut, konjac, cowhide, sheepskin, leather shoes, the implementation of 20 kinds of products such as import quotas tariff management, which is a tax levied on imports only in limited scope, including zero tariff, lower tariffs, imposing high tariffs. In addition, under bilateral economic co-operation agreements, Japan has imposed quota tariffs on 16 products, including tomato concentrate from Mexico, and fresh bananas from Malaysia.
Import goods by tariff quota system regulation, when the import declaration must submit the certificate of tariff quotas to the Japanese customs, according to Japan and other countries or economies signed economic cooperation agreement, in some cases the relevant ministries and agencies also to Japan's exports to the country or economy quota control goods exporters of tariff quotas certificate. With the effect of TPP11, Japan began to gradually reduce the import tariffs on agricultural products to Australia, Canada, Chile, New Zealand and other countries, and relax the import quota restrictions on their agricultural products.
[Export Restriction] The export of specific goods can only be exported after referring to relevant laws and regulations and obtaining approval. Relevant reference website:
www.customs.go.jp/tetsuzuki/c-answer/extsukan/5501_jr.htm
7.1.4 Inspection and quarantine of import and export commodities
[Inspection and Quarantine of Agricultural Products] Japan has developed the strictest inspection and quarantine standards for food in the world. In May 2006, according to the food hygiene law of the residues of pesticides in food, feed additive and animal medication implemented a "definite list system", the system provides more than 50000 of the 799 kinds of agricultural chemicals in various agricultural products remain the lowest limit, shall be implemented for the rest of the provision of the specific standards for the project will be turned over to the standard of 0.01 PPM. The Japanese government on imported agricultural products set up a predominantly through monitor and check our command monitoring system, regulation of losing 10% of the agricultural products to monitor examination spot-check proportion, found that overweight is increased sampling rate to 50%, and for more than two found excessive amounts of the same chemical residues of agricultural implement one hundred percent check command to check.
[Animal Quarantine] According to the Law on the Prevention of Infectious Diseases in Livestock, Japan carries out strict inspection and quarantine on animals and livestock products imported from abroad. To carry out designated inspections on artiodactyls, horses and their manufactured products, chickens, quails, ostriches, turkeys and ducks and their eggs; The ban on the import of artiodactoed ungulates and their manufactured products from or through "epidemic areas" such as Europe, Asia and the United States; Imports of poultry and poultry meat outside the designated inspection targets will be prohibited from all countries or regions that have experienced a high level of avian influenza. Japan divides the animal diseases that it focuses on prevention into two categories, one is "livestock infectious diseases", a total of 26 kinds, and the other is "declared infectious diseases", a total of 71 kinds. These two types of diseases are collectively called "surveillance infectious diseases". In recent years, with the spread of African swine fever, the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries of Japan updated the Law on Prevention of Infectious Diseases in Livestock and took effect on April 22, 2019. According to the Law on the Prevention of Infectious Diseases in Livestock, those who bring livestock products into Japan without being quarantined will be punished with up to three years in prison or a fine of up to one million yen.
The Animal Quarantine Institute is a subordinate department of the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries. The Institute is located in Yokohama and has branches in Narita, Chubu Airport, Kansai Airport, Kobe and Okinawa. There are police stations in Hokkaido chitose, sendai, niigata, Tokyo, shimizu, haneda, Nagoya, komatsu, komatsushima, Osaka, okayama, Hiroshima, harata, fukuoka, Nagasaki, kagoshima and naha.
[Phytosanitary] Japan conducts quarantine on imported plants in accordance with the Plant Quarantine Law. Japan prohibits the import of invasive plants, harmful plants and plants with soil attachment. The import of some prohibited plants is allowed on the premise that the inspection and quarantine certificate can be provided; Some prohibited plants (such as Chinese straw) may be imported when the site is inspected by the Japanese quarantine officer and the quarantine certificate issued by the Japanese and Chinese government authorities is obtained; The introduction of cultivation seedlings in Japan will be 1-2 years of isolation cultivation quarantine; A quarantine certificate issued by the government agency of the exporting country is required for the import of general plants or, if there is no government agency for phytosanitary inspection in the exporting country, by the Japanese Plant Quarantine Station at the time of import; Wood, furniture, cotton, paper and other products made from highly processed plants do not require phytosanitary treatment.
Quarantine procedure: first, the importer submits the application for plant and animal quarantine inspection. If any, the importer can submit the phytosanitary inspection certificate of the exporting country. Then, the quarantine officer will visually check whether there are diseases, insects and pests attached, or carry out sampling inspection. If not found, a certificate of conformity is issued and customs clearance can be carried out. If found, a certificate of conformity can be issued after disinfection treatment, or the disposal can be abandoned and returned to the original importing country. The animal quarantine procedure is the same.
Phytosanitary inspection is carried out by the Phytosanitary Institute of the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries, which is located in Yokohama, Nagoya, Kobe, Moji and Naha. Although the Ministry of Health, Labour and Health also conducts quarantine, it only applies to food to ensure food safety.
[Main Quarantine Measures Affecting China] At present, "Positive List System" has become the biggest factor affecting the export of Chinese agricultural products to Japan. At the same time, after a long negotiation, the Chinese government and the Japanese government and Chinese enterprises in the Japan market for many years of arduous pioneering and fumble, in recent years, the Japanese government opened up appropriate for China, the limitation of poultry meat and fruit products, designated area production part of the agricultural products such as straw, pumpkin has can enter the Japanese market.
7.1.5 Customs management rules and regulations
Tariff Law, Tariff Rating Law, Tariff Provisional Measures Law and Tariff Rate Schedule constitute the basic tariff-related legal system in Japan. The Tariff Act is the law concerning the collection and payment of customs duties and customs clearance. The Law of Tariffs Act, enacted in 1911, is the only effective pre-war customs law. It is a highly technical regulation of how to determine tariff rates, tax standards and exemptions. The Interim Tariff Measures Act is to meet the needs of tariff policy adjustment under the new situation of the rapid development of foreign trade under the background of rapid economic growth after Japan's accession to GATT.
Tariff Rating Table, namely Customs Tariff Rules, is the rules and tariff rate classification table formulated and published by a country for levying customs duties on inbound and outbound goods. The table contains the detailed names, tariff rates, tariff standards (AD valorem or specific quantity), tax units, etc., of the goods taxed or exempted. In 1988, after Japan became a contracting party of the Convention on Harmonized System, it began to use the Harmonized System of Commodity Names and Coding (HS) system to make tax rules. The tariff number is 9 digits in international common use, and the tariff is divided into 21 parts and 97 categories. Tariff rate by basic rate, the temporary tariff rate, the WTO agreement rate, pratt &whitney tax rates and preferential rates (Japan for general unilateral preferential tax rate of developing countries, also including against one of the most underdeveloped countries special preferential tariff of LDC), in addition, signed free trade agreement with Japan's national customs tariff single within the tariff. The decision process of tariff rate is divided into two stages, one is commodity classification, the other is the origin of goods. On the whole, except for agricultural products, a few luxury goods and some special goods, Japan has low tariff or no tariff. Non-tariff goods account for about 40% of the total categories of goods, and Japan is a country with a high degree of openness in the world. Attached is the tariff rate table of major imported commodities with high personal interest:
Tariff Schedule of Major Imports of Japan (from 1 April 2019 to present)
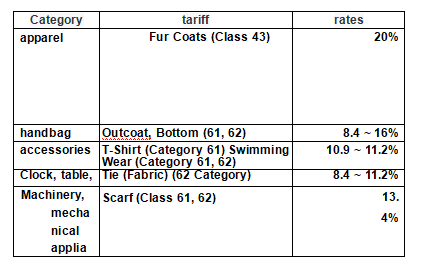

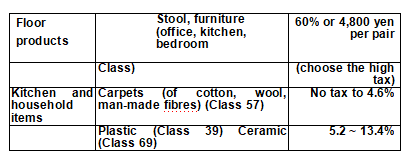
Note: the classification order of Japan's Tariff Rating Table is division and category, and the categories and chapters corresponding to China's tariff rules, that is, category 43 is chapter 43 of China's tariff rules. Because the tariff rate and the tariff rate of each commodity varies greatly due to the country of origin, the material of the commodity, whether there is processing or use, etc., the tariff rate in this table cannot be simply applied, for reference only. The specific tax query address: http://www.customs.go.jp/tariff/2019_4/index.htm
- Frame section: exhibition (food)
1) 2021 Japan Food Exhibition
http://www.yshows.cn/zhanhui/397.shtml?from=singlemessage
The basic information
Name (English) : Foodex Japan, 46th International Food and Beverage Exhibition in 2021
Name: Foodex Japan
Exhibition Date: July 14, 2021 - July 16, 2021
Venue: Tokyo, Japan
Exhibition cycle: once a year
Organizer: Japan Management Association
Organizer: Beijing Zhongling International Exhibition Co., Ltd
Industry attributes
Food, beverage, alcohol, tobacco
Exhibits range
(1) Fresh food: meat, processed meat, fish, dried salted products, fruits, etc.;
(2) Processes food: cereals, condiments, noodles, prepared meals, cooling, chestnuts, snack food, frozen food, dairy products, bread, tofu, quality food, etc.;
(3) Beverages: all kinds of alcoholic drinks, non-alcoholic drinks, coffee, black tea, mineral water, Japanese tea and other tea, health drinks, etc.
The exhibition to introduce
※ Japan International Food and Beverage Exhibition, held once a year, is the largest, most prestigious, most complete and most traded food exhibition in the Asia-Pacific region. It is the third largest food and beverage exhibition in the world, only next to Germany's ANUGA and France's SIAL. The exhibition has been held annually since 1976 and will be held for the 42nd time in 2017. As the best place for both exhibitors and visitors to explore business opportunities, it has always been highly praised by relevant people.
※ Previous review:
In 2015, the exhibition booth area was 29,902 square meters, and a total of 2,977 exhibitors from 62 countries came to participate in the exhibition. Among them, Japanese exhibitors accounted for 28%, and the other 72% were from overseas exhibitors. During the exhibition, 77,361 people came to the museum to visit and negotiate, 70% of which were professional visitors from the company management. Japan is the world's largest importer, with a self-sufficiency rate of less than 40% and imports worth $42 billion in 2002. In addition, Japan is the second largest economic power in the world, in every way to walk in front of the world, the food industry is no exception, to participate in the exhibition can learn the latest information and the latest development of industry in the world, also can directly to carry out the corporate image promotion, publicity of brand strategy, and directly to carry out the sales promotion and trade negotiation activities. To sum up, participating in Japan International Food and Beverage Exhibition is undoubtedly the best platform for enterprises to seek trade partners, promote products and develop the Japanese market.
In 2016, there were 3,197 exhibitors and 76,532 visitors
The market background
※ Japan is highly dependent on imports. At present, its self-sufficiency rate of agricultural products is about 40%. Japan imports about 70 billion US dollars of food every year. Earthquake and tsunami caused serious damage to a large area of land in Japan, will give Japan in the future for a long period of time caused immeasurable damage to agriculture. At present, Japan's Fukushima, Miyagi, Iwate and other counties rich in rice, aquatic products, fruits and other losses are the most disastrous. Miyazaki Prefecture, Fukushima Prefecture and Tochigi Prefecture, which are the main vegetable bases in the Japanese capital region, will not be able to produce normally for the next three years. Japan's poultry breeding and processing industry is mainly distributed in the Northeast region, which was badly affected by the nuclear radiation. Considering the long-term impact of nuclear radiation, the production of chicken products in Japan will take more than three years to recover, which is an opportunity for China's chicken products export.
※ According to statistics, orders from Japan have doubled since the earthquake, including frozen vegetables, water, seafood, canned vegetables, boiled vegetables and salted vegetables. At the same time, Chinese mineral water also entered the Japanese market this time. Chinese enterprises should take the initiative to grasp the nuclear leakage accident brought part of the agricultural products market vacancy, take the opportunity to expand the export space of Chinese agricultural products.
- Frame section: food category
General Situation of Japanese Sake: According to Chinese historical records, there was only "turbidity wine" in ancient Japan, and there was no sake. Later, some people added charcoal to muddy wine to precipitate it, and then drank the pure liquor, thus getting the name "sake". After the middle of the 7th century AD, the ancient state of Paikche of Korea had frequent contacts with China and served as a bridge for the spread of Chinese culture to Japan. Therefore, the Chinese technique of making wine with "quzhong" was spread to Japan by the Paikche people, which made great progress and development of Japanese brewing industry. By the 14th century, Japan's brewing technology had become increasingly mature, and people used the traditional sake brewing method to produce high-quality products. This is known as "monk wine", the most famous of which is produced especially in the Nara region. Later, the "monk wine" was abandoned, and the brewing center was transferred to the "Shingquan 12 Township", mainly in Idan, Kobe and Nishimiya. In the late Meiji period, it was transferred from the "Shingquan 12 Townships" to the "Beach Five Townships" consisting of Kobe and Nishimiya. Beach five townships from the late Meiji period has been retained "Japan's first wine country" status. Now there are more than 1500 sake breweries of all sizes in Japan.
Exports to China:
According to data provided by the Japan Sake and Shochu Manufacturers Association to Jiemian News, currently, Bunge Shochu and Soo Shin are exporting more to China, with a total export amount of 1.5 billion yen in 2018, of which the Chinese mainland accounts for 31.1% and the US market 25.7%, and China is its largest exporter. In terms of Japanese liquor, the United States is currently the largest exporter of Japanese liquor. In 2018, the total export value of Japanese liquor was 22.2 billion yen, of which the US market accounted for 28.4%, the Chinese mainland 16.1%, and Hong Kong 17%. Mainland China is soon expected to overtake the US market as the biggest export of Japanese liquor.
- Frame section: brand recommendation
1, 14 generations (Yamagata Takagi wine, is popular in recent years, "aromatic and mellow mouth" on behalf of wine)
- Flower Yang Bath (Nanyang Wine, Flower Yang Bath is the representative work of Nanyang Wine in Saitama Prefecture, Japan)
- Now (This series of sake is perfect for meat, fish such as shrimp, sea urchin, etc., and also matches well with Italian cuisine)
- New Deal Series No. 6 (New Deal Jiuzao, New Deal Jiuzao is not a new winery, but a traditional winery with a history of more than a hundred years)
- Huayi (struck guan wine)
6, Xinzhou turtle age
- Kawanaka Island Magic Dance
New Deal Sky Frog
- Yang Nai Bird (Young Bird, this is also a wine made from New Deal wine, which was first released in the "Private Lab" series)
10, ソガ · Zha · Chao · Shi (made by Nagano Small Bushi Wine)
- Frame section: enterprise recommendation
Kobe chrysanthemum is authentic
The eastern part of Kobe City (Tan District, Dongtan District) is located along the coast. Among the five villages known as "Beach Wine", there are Fishaki Township, Oying Township and Nishixiang Township. Now still retains the wine of the past way, can feel the scene at that time. Several winemaking companies are open to the public as libraries, as well as tasting wines and places to party.
Chrysanthemum authentic brewing memorial was built in 1659 (million to 2) years, for the Royal Shadow Township "this Jia Na house" in the house of wine, Showa 35 years to move to the present site. The museum is mainly a museum to introduce Japanese wine culture. There are a large number of important cultural relics related to Japanese wine, such as various tools for making wine, posters, signboards and drinking utensils. The museum also has a wine tasting area and a small shop where visitors can sample a variety of Japanese sake and choose on the spot.
Kyoto Month Laurel
YUE KWAN Sake is a brand of YUE KWAN CO., LTD., which was established in 1637 (HWA 14). The domestic product is sold by Taiwan weedan company. In 1637 (the 14th year of Kwanaga), the first generation of Okura Jimon came to Kyoto Fumie from Kasa Machi (now Kasa Machi in Sagura Prefecture) in the south of the capital city and started his business. The business name is "Li Zhiwu", and the wine name is "Jade Spring". During the Meiji era, science and technology were introduced in winemaking, with preservative-free bottles introduced during the heyday of cask wine. In 1910 (Meiji 43), the "small bottle with cup" was developed and adopted as the "station selling wine" during the railway academy era, which became the opportunity for the month laurel to become widely known. Later, with the aim of "quality first", it adopted the four-season brewing system of year-round brewing for the first time in Japan, and made use of new technology to produce high-quality wine. In recent years, Japan has transferred its mature Four Seasons brewing system and new brewing methods to the United States, and opened local wine cellars in an effort to supply sake to the world.
- Professional data
- Frame: national and food data
(1) Japanese food has obtained halal certification, and sales channels have been expanded
https://www.cifnews.com/article/7553
(2) Infomart, a Japanese food e-commerce giant, has entered into China strongly and formed a strategic partnership with Nimetong
https://www.cifnews.com/article/15341
(3) Japanese food is famous overseas. Postal fresh delivery helps cross-border fresh electricity suppliers
https://www.cifnews.com/article/20599
(4) Announcement of the General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China on Further Strengthening the Inspection and Quarantine of Food and Agricultural Products Imported from Japan (Announcement of the General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China No. 44, 2011)
http://law.foodmate.net/show-188840.html
(5) The latest data of the functional food market in Japan: the functional expressive food market increased by 25.9 percent, and lactic acid bacteria, black ginger and other raw materials were concerned
https://news.21food.cn/35/2900138.html
Japan Food Analysis Center
https://www.jfrl.or.jp/chinese
Statistics of Japan's seafood import and export data in November 2020
http://news.foodmate.net/2021/01/583539.html
Chinese Embassy and Consulate General in Japan
Embassy in Japan
Ambassador: Kong Xuanyou
Address: 3-4-33 Motozabu, Tokyoku, Japan
3-4-33 Moto-Azabu, Minato-ku, Tokyo, Japan
Zip code: 106-0046
Telephone: 0081-3-3403-3388
Fax: 0081-3-3403-3345
Consular Section 0081-3-3403-5447
Website: http://www.china-embassy.or.jp
http://jp.china-embassy.org
http://jp.chineseembassy.org
E-mail: INFO@CHINA-EMBASSY.OR.JP
Economic and Commercial Affairs Office of the Chinese Embassy in Japan Address: 5-8-16 Minamazu, Kondo District, Tokyo, Japan
Telephone: 0081-3-3440-2011
Fax: 0081-3-3446-8242
Address: jp. Mofcom. Gov. Cn/index. SHTML email: jp@mofcom.gov.cn
Consulate General in Niigata (Japan)
Consulate-general OF THE People's Republic OF China IN Niigata
Consul General: Sun Dagang
Address: 5220-18, nisisahata, chongyuku, niigata prefecture
5220-18, Nishiohata-cho, Chuo-ku, Niigata,951-8104,Japan
Zip code: 950-8104
Country code: 0081-25
Telephone:
Operator: 0081-25-228-8888, 0081-25-228-8901 (Fax)
Office: 0081-25-228-8800
Political and Cultural Section: 0081-25-228-8885
Overseas Chinese Section: 0081-25-228-8899, 0081-25-228-8887, 0081-25-228-8818 (Fax)
Business Section: 0081-25-228-8898
Education Section: 0081-25-228-8878
Website: http://niigata.china-consulate.org
E-mail: chinaconsul_nii_jp@mfa.gov.cn
Economic and Commercial Office, Consulate General of China in Niigata
Address: 5220-18, Nisisahata, Chuo-ku, Niigata, Niigata, Japan Tel: 0081-25-228-8888
Fax: 0081-25-228-8901
Address: niigata.china-consulate.org/chn
Consulate-General in Sapporo (Japan)
CONSULATE-GENERAL OF THE PEOPLE'S REPUBLIC OF CHINA IN SAPPORO
Consul General: Liu Yaming (female)
Consulate General of the People's Republic of China in Sapporo
5-1, Nishi 23-chome, Minam 13-j0, Chuo-ku, Sapporo, Japan
Telephone: 0081-11-563-5563
Fax: 0081-11-563-1818
Website: http://www.chn-consulate-sapporo.or.jp
http://sapporo.china-consulate.org
http://sapporo.chineseconsulate.org
E-mail: chinaconsul_sap_jp@mfa.gov.cn
Economic and Commercial Office, Consulate General of China in Sapporo
Address: Nishi 23-5-1, Minami-13, Chuo-ku, Sapporo, Japan Tel: 0081-11-563-5563
Fax: 0081-11-563-1818
Address: Sapporo. Mofcom. Gov. Cn/index. SHTML
Consulate-General Nagasaki (Japan)
Consulate-general OF THE People's Republic OF China IN Nagasaki
Master:
Address: Chu 852 10-35 Hashiguchi Machi Nagasaki, City Japan
Telephone: 0081-958-4933 11
Fax: 12 0081-958-4933
Website: http://nagasaki.china-consulate.org
http://nagasaki.chineseconsulate.org
E-mail: chinaconsul_nag_jp@mfa.gov.cn
Consulate-General in Fukuoka (Japan)
CONSULATE-GENERAL OF THE PEOPLE'S REPUBLIC OF CHINA IN FUKUOKA
Consul General: LV Guijun
Address: Fukuoka-Shi Chuo-Ku Jigyohama 1-3-3, Japan
Country code: 0081-92
Telephone: 7131121
Fax: 7818906
Website: http://fukuoka.china-consulate.org
http://fukuoka.chineseconsulate.org
E-mail: chinaconsul_fuk_jp@mfa.gov.cn
Commercial Science and Technology Section, Consulate-General of China in Fukuoka
Address: 1-3-3, Chiyohama, Chuo-ku, Fukuoka, Japan Tel: 0081-92-713-1121
Fax: 0081-92-781-8906
Address: fukuoka. Mofcom. Gov. Cn/index. SHTML
Consulate-General in Nagoya (Japan)
CONSULATE-GENERAL OF THE PEOPLE'S REPUBLIC OF CHINA IN NAGOYA
Consul General: Liu Xiaojun
Address: 2-8-37 Higashisakura, Higashi-Ku, Nagoya, Aichi, 461-0005 Japan
Telephone: + 81-52-9321098
Fax: + 81-52-9321169
Website: http://nagoya.chineseconsulate.org/
http://nagoya.china-consulate.org/
Bilateral Section of the Chinese Consulate-General in Nagoya
Address: Kondo 2-8-37, Nagoya City, Nagoya Prefecture, Japan Tel: 0081-52-932-1098
Fax: 0081-52-932-1169
Address: nagoya.china-consulate.org/chn
Consulate-General Osaka (Japan)
CONSULATE-GENERAL OF THE PEOPLE'S REPUBLIC OF CHINA IN OSAKA
Consul General: He Zhenliang
Address: 3-9-2 Honcho, 靱, West District, Osaka-shi
3-9-2 Utsubohonmachi Nishiku 0Saka, Japan ASE 550-0004
Country code: 00816
Telephone:
Room: 64459481,64459482
Political and cultural exchanges: 64459472,64459476 (Fax)
Business: 64459471,64459478 (Fax)
Overseas Chinese Affairs: 64459470,64459480 (Fax)
Passport, Visa: 64459483,64459480 (Fax)
General Affairs: 64459473,64459475 (Fax)
Education: 68212301,68212303 (fax)
Website: http://osaka.china-consulate.org
http://osaka.chineseconsulate.org
E-mail: chinaconsul_osa_jp@mfa.gov.cn
Economic and Commercial Office, Consulate General of China in Osaka
Address: 3-9-2, Honcho, Osaka City, Osaka Prefecture, Japan. Tel: 0081-6-6455-9481
Fax: 0081-6-6445-9475
Address: Osaka. Mofcom. Gov. Cn/index. SHTML
- Japanese Embassy and Consulate General in China
Japanese Embassy in China
Embassy of Japan
Chancery: No. 1, East Liangmaqiao Street
Chancery: No. 1, Liang Ma Qiao Dong Jie
Telephone: 85319800 (Operator)
Fax: 65327081
Consular Office of Japan Consulate General in Shenyang in Dalian
Dalian Consular Office of the Consulate General of Japan in Shenyang
Chancery: 3 / F, Senmao Building, 147 Zhongshan Road, Xigang District, Dalian City, Liaoning Province
Chancery: 3F, Senmao Building, 147 Zhongshan Road, Xigang District, Dalian, Liaonig Province
Telephone: 0411-83704077
Fax: 0411-83704066
Area: Dalian
DISTRICT, Dalian
Consulate General of Japan in Chongqing
Consulate General of Japan in Chongqing
Chancery: 42nd Floor, World Financial Center, 188 Minzu Road, Yuzhong District, Chongqing
Chancery: 42F, Chongqing World Financial Center, 188 Minzu Road, Yuzhong District, Chongqing
Tel: 023-63733585
Fax: 023-63733589
Region: Chongqing, Sichuan, Guizhou, Yunnan, Shaanxi
District: Chongqing, Sichuan, Guizhou, Yunnan, Shaanxi
Consulate General of Japan in Shenyang
Consulate General of Japan in Shenyang
Office address: No. 50, Shiwei Road, Heping District, Shenyang, Liaoning
Chancery: 50 Shisiwei Road, Heping District, Shenzhen, Liaoning Province
Tel: 024-23227490
Fax: 024-23222394
Area: Liaoning, Jilin, Heilongjiang
District: Liaoning, Jilin, Heilongjiang
Consulate General of Japan in Guangzhou
Consulate General of Japan in Guangzhou
Chancery: 1-3 / F, Garden Building, 368 Huanshi East Road, Guangzhou City, Guangdong Province
Chancery: 1-3F Garden Tower, 368 Huanshi Dong Lu, Guangzhou, Guangdong Province
Telephone: 020-83343009
Fax: 020-83338972
Region: Guangdong, Guangxi, Fujian, Hainan
District: Guangdong, Guangxi, Fujian, Hainan
Consulate General of Japan in Qingdao
Consulate General of Japan in Qingdao
Chancery: 45F, International Finance Center, 59 HongKong Zhong Lu, Qingdao City, Shandong Province
Chancery: 45F, Qingdao International Finance Center, 59 Hongkong Middle Road, Qingdao, Shandong Province
Tel: 0532-80900001
Fax: 0532-80900009
Region: Shandong Province
DISTRICT: Shandong
Consulate General of Japan in Shanghai
Consulate General of Japan in Shanghai
Chancery: 8 Wanshan Road, Shanghai
Chancery: 8 Wanshan Road, Shanghai
Tel: 021-52574766
Fax: 021-62099110
Region: Shanghai, Zhejiang, Jiangsu, Anhui, Jiangxi
District: Shanghai, Zhejiang, Jiangsu, Anhui, Jiangsu
- Economic and Trade Institutions (Chamber of Commerce)
(1) Japan Organization for the Promotion of Trade
Founded in 1958 and funded by the Japanese government, the agency promotes trade and investment. In 1998, it was merged with the Institute of Asian Economics into a special legal entity. In October 2003, it was renamed as an independent administrative entity, Japan Organization for the Promotion of Trade, under the supervision of the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry of Japan. The current president is Nobuhiko Sasaki.
The agency supports foreign investment in Japan, promotes the export of Japanese agricultural, forestry, aquatic and food products, supports Japanese small and medium-sized enterprises to conduct overseas business, conducts investigations and studies on trade and investment issues, and supports foreign enterprises to conduct economic cooperation with Japanese enterprises.
Tokyo headquarters
Address: 1-12-32 Arksen Building, Akasaka, Tokyoku, 107-6006, Japan
Tel: 0081-3-35825181 Fax: 0081-3-35828309
Beijing Representative Office
Address: Room 7003, Changfu Palace Office Building, No. A, Jianguomenwai Street, Chaoyang District, Beijing
Fax: 010-65137079
Shanghai Representative Office
Address: 21F, Shanghai International Trade Center, No. 2201, Yan 'an West Road, Changning District, Shanghai Tel: 021-62700489
Fax: 021-62700499
Dalian Representative Office
Address: 19 / F, Senmao Building, No.147 Zhongshan Road, Xigang District, Dalian City, Liaoning Province
Fax: 0411-83609498
Guangzhou Representative Office
Address: Room 2601, CITIC Plaza, No. 233, North Tianhe Road, Tianhe District, Guangzhou City, Guangdong Province
Fax: 020-87520077
Qingdao Representative Office
Address: Room 12-D, Qingdao Ocean Building, No. 61 Hong Kong Middle Road, Shinan District, Qingdao City, Shandong Province
Fax: 0532-83878900
Wuhan Representative Office
Add: 12 / F, Building A, New World Center, No. 634, Jiefang Avenue, Qiaokou District, Wuhan City, Hubei Province
Fax: 027-83590726
Chengdu Representative Office
Address: Room 03, Floor 20, Building 2, Chengdu Raffles Plaza Office Tower, No.3, Section 4, South Renmin Road, Wuhou District, Chengdu City, Sichuan Province
Tel: 028-8779-6693 Fax: 028-8763-3752
Hong Kong Representative Office
Room4001,40/F., Hopewell Centre,183 Queen's Road East,
Wan Chai, Hong Kong Tel: 00852-2526-4067 Fax: 00852-2868-1455
(2) Japanese economic and trade groups to China
Japan Association for the Promotion of International Trade website: http://www.japitcn.com
Address: 4 / F, Persimuma Building, No. 13, No. 9-1, Uchiyoda, Chiyoda District, Tokyo, Japan; Tel:0081-3-6740-8261Fax:0081-3-6740-6160 Email:somu@japit.or.jp
Website of Japan-China Economic Association: http://www.jc-web.or.jp
Address: 6F, Roppongi Asabutai Building, MFPR, No. 7, 1 Timoku 8, Roppongi Dockaku, Tokyo, Japan; Fax :0081-3‐5545-3117 Email:webmaster.jcea@jc-web.or.jp
Japan-china economic and trade center web site: http://www.japanchina.jp/
Address: 2F, Osaka Center Building, 1-3 No.4, Kutaro Machi, Chuo-ku, Osaka-shi, Japan; Tel:0081-06-4704-2511 Fax:0081-06-4704-2512 E-mail:jcc@mail.infomart.or.jp
Website of Japan-China Investment Promotion Agency: http://jcipo.org/
Address: Fuji 1-1-8 Chiyoda District, Tokyo, Japan Fuji Bldg2 floor; Zip: 102-0071 Tel:0081-3-5226-0141 Fax:0081-3-5226-0143 Email:info@jcipo.org
Kyoto, Japan association for the promotion of international trade administration website: http://www.japitkyoto.jp/
Address: No. 5 Nagaya BLDG 3F, 637 Xiashuiya-cho, Umarutsu Sitiashuiya-cho, Shimagyo District, Kyoto City; Zip code: 600-8411 0081-75-3540777 Fax:0081-75-3540778 E-mail:kyotosou@mbox.kyoto-inet.or.jp
Website of East China Sea Japan China Trade Center: http://www.tokai-center.or.jp/
Address: 6F, Koya Chamber of Commerce and Industry Building, No. 2-10-19, Nakao-District, Nagoya, Aichi Prefecture, Japan; Zip :460-0008 Tel:0081-52-2194820 Fax:0081-52-2194823 E-mail:tokai-gyoumu@mtb.biglobe.ne.jp
 |
 |
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
 |
 |
||
 |
|||||