EFL · National City (Ukraine)
(1) Ukrainian national

- Signature Architecture: The Statue of the Motherland Mother

[Name] Ukraine (Ukraine,Украина)
[Location] Located in eastern Europe, on the north shore of the Black Sea and the Sea of Azov. It borders Belarus in the north, Russia in the northeast, Poland, Slovakia, Hungary in the west, and Romania and Moldova in the south.
[Area] 603,700 sq.
[Population] 41.58 million (January 2021, excluding Crimea).
[Capital] Kiev (Kyiv,Киев), with a population of 2.96 million.
[Ethnic] More than 110 ethnic groups, 77% Ukrainian and 17% Russian.
[Language] The official language is Ukrainian and widely used in Russian.
[Religion] Mainly believed in the Orthodox Church and Catholicism.
[National Day] August 24th.
[Currency] Griffner, 1 U. S. ≈ 27.73 Griffner.
[Administrative divisions] The country is divided into 24 states, 1 autonomous Republic (Republic of Crimea) and 2 municipalities (capital Kiev and Sevastopol).
In the early Paleolithic period, there were traces of ancient human activities existing in the present territory of Ukraine. The term "Ukraine" was first seen in the Ross Records (1187) meaning "frontier land". In 1240, the Mongol Imperial Expeditionary Force (Batu) occupied Kiev. Later the Mongol Golden Khanate, the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and Poland ruled Ukraine. In 1654, the Ukrainian Cossack leader signed the Pelyaslav Contract with the Russian tsar, and Ukraine and Russia were formally merged. Since then, Ukraine has had its own government, but it has not played a substantial role. Joining the Soviet Union in 1922 (Western Ukraine joined in 1939). On 16 July 1990, the Supreme Soviet of Ukraine adopted the Declaration of the National Sovereignty of Ukraine. Then on August 24,1991, Ukraine declared its independence.
[Constitution] On 28 June 1996, the Ukrainian parliament passed its first constitution after independence, establishing Ukraine as a sovereign, independent and democratic state of law, and implementing a republican system. The President is the Supreme Head of State representing the State; the Supreme Rada (Parliament) is the legislature; the Government is the executive and is responsible to the President. After independence, Ukraine's political system has changed repeatedly between the parliamentary presidential system and the presidential parliamentary system, now the parliamentary presidential system.
[Parliament] Ukraine 's parliament called the "Supreme Rada", the country' s highest legislature, with a unicameral system of 450 seats, with a five-year term, half of the seats elected by parties and half directly elected by the district. There is 1 speaker, 1 first deputy speaker and 1 deputy speaker. In July 2019, the ninth (nonroutine) parliamentary elections were held in Ukraine, with President Zelinsky 's "public servant" Party, Boyko' s "opposition platform-for life" Party, former Prime Minister Tymoshenko's Motherland Party, the "European Unity" Party led by former President Poroshenko, and the "voice" Party led by singer Wakalchuk.
[President] The President is the supreme head of state representing the state, directly elected for a five-year term, but not more than two terms. President Vladimir Zelensky,Владимир Зеленскии, who took office in May 2019, and served until 2024. Prime Minister Denis Shmygal,Денис Шмыгаль, who took office in March 2020.
[Government] Under Ukrainian government law, the government is the highest power executive body of the state and is responsible to the president. The government candidate for premier is nominated by the President on the recommendation of the parliamentary majority and appointed by Parliament. If the president does not nominate a Prime Minister candidate to Parliament within the statutory period, Parliament will appoint the Prime Minister based on the nomination of the majority. The government was formed in March 2020, including the Prime Minister, four deputy prime ministers, and 16 ministers.
[Politics] On 21 April 2019, Ukraine held the second round of the new presidential election, with actor Zelensky got 73.19% of the vote elected and took office on May 20. On 21 July, the ninth (non-routine) parliamentary elections were held in Ukraine. President Zelensky's PPP Party won 254 of the 450 seats and won separate powers. Zelensky and his new government promoted reform internally, adhered to the policy of joining contracts externally, and actively improved relations with Russia.
On 4 March 2020, Ukrainian Prime Minister Gonzaluk resigned and Deputy Prime Minister Shmear, former director of community and territorial development, served as Prime Minister.
[Judicial Agency] The Ukraine's judicial system consists of constitutional courts, courts and procuratorates. The Constitutional Court is the supreme judicial body that upholding the Constitution. The judgment of the Constitutional Court is final and is not appealable. The Ukrainian court system is composed of ordinary and specialized courts. The highest judicial organ of the General Court is the Supreme Court of Ukraine. The supreme trial organ of the specialized court is the corresponding Supreme Court. The courts is the only body exercising exercise trial power. Ukraine's constitution and law guarantee the independence and exclusion of the judges. Judges adopt a lifelong tenure system. The procuratorate system is composed of the Supreme Procuratorate of Ukraine, the state procuratorates and the district procuratorates.
[Political Parties] Ukraine has a multi-party system. As of 1 January 2020, there were 349 parties registered in the Ukrainian Ministry of Justice, but only about 30 were more active and 22 parties participating in the 9th parliamentary elections. Ukrainian political parties often unite, divide, renamed and reorganize around parliamentary elections, with a precarious voter base. Mainstream ideology is pro-europeanism and liberalism, and populist thought has risen in recent years. The 2019 parliamentary elections included 5 parties to the 9th Parliament.
[Mineral Resources] Ukraine is rich in mineral resources, and has identified more than 80 kinds of rich minerals available for mining, mainly coal, iron, manganese, nickel, titanium, uranium, mercury, graphite, refractory soil, stone, etc., widely distributed in more than 7,000 producing areas in China, among which more than 4,000 regions have been developed. More than 2.18 billion tons of manganese ore is the top in the world; iron ore reserves are about 27.5 billion tons and coal, fuel ore, clay, earth wax and graphite. Oil and natural gas resources are relatively scarce and have high external dependence, among which, 2019 m 3 of 20.7 billion m 3, year-on-year decrease of 1.4%, 14.2 billion m 3,34.9%, 1.99 million tons in 2019,5.7%, 790,000 tons, a year-on-year increase of 3.1%.
Ukraine's coal reserves are 44.734 billion tons, including 41.49 billion tons of hard coal and 2.594 billion tons of lignite. Affected by the conflict in Donbass, the coal production in Ukraine has declined year after year, mining 31.21 million tons in 2019, down 6.2% year on year.
[Agricultural resources] Ukraine is rich in agricultural resources, with a black soil area accounting for 27% of the world's total black soil. Agricultural land area is 42.73 million hectares, or 55.5% of the forest land area, and 10.63 million hectares, or 17.6% of the forest land area. In 2019, the primary industry output value accounted for about 9% of the GDP.
[Water resources] Ukraine has sufficient water resources, with 23,000 rivers and all sizes, more than 20,000 lakes, and more than 100 rivers with a length of more than 100 kilometers.
[Animal and Plant Resources] Ukraine is rich in plant resources, with a forest coverage rate of 15.9%. There are about 30,000 species of low and advanced plants. The main tree species are: pine, tussah, spruce, fir, linden, maple, birch, etc. There are about 44,800 species of animals, including the territorial sea waters of the Black Sea and the Sea of Azov.
[Economy] At the end of 2013, the second "square revolution" broke out in Ukraine, and the political and economic situation was violently turbulent. Influenced by factors like the Eastern War, the economy declined sharply from 2014 to 2015 (the actual GDP fell 6.8% in 2014 and 9.9% in 2015). Continusustained positive growth from 2016-2019. The main factors restricting Ukraine's economic growth are: first, the frequent government changes; second, the drag of the eastern conflict; third, the single economic structure, the low added value of the leading industrial products and the weak competitiveness; fourth, the poor business environment and the weak investment.
In 2019, Ukraine's economy maintained growth with nominal GDP 3974.564 million Griffner, actual GDP 3675.728 million, 3.2% and nominal GDP 94,590 Griffner per capita. In 2019, Ukraine's macroeconomic overall was stable and continued to maintain low growth. According to the Ukrainian National Statistics Agency, the total Ukrainian GDP was 3.97 trillion (for about $ 153.5 billion), up 3.2% year on year. Foreign trade was US $ 110.79 billion, a 6% year-on-year increase. The total national debt share of GDP fell to 50% for the first time in five years. Inflation rate was 4.1%, the lowest level in the last five years. Unemployment rate fell to 8.6%. The financial sector was generally stable, and the national bank discount rate continued to decrease, down to 13.5% at the end of late 2019. But the industrial production index declined for three consecutive years, and the real economy was weak. In 2020, Ukraine was USD 103.6 billion, with exports of USD 49.3 billion, down 1.7% year on year, and USD 54.2 billion, down 10 year on year. 2%. In January-September 2020, the Ukrainian economy was hit hard by COVID-19, with GDP down 5.6%, inflation of 5% and unemployment of 9.7%.
[Foreign Trade] On 16 May 2008, Ukraine joined the World Trade Organization. On September 20,2012, some bilateral agreements on the CIS FTA by Ukraine came into effect. On 27 June 2014, Ukraine signed the contact countries agreement with the EU, and the —— began on 1 January 2016. In 2019, the Ukrainian trade in foreign goods totaled US $ 110.85 billion, a 6.4% year-on-year increase. Of these, exports were $ 50.05 billion, up 5.7%; imports were $ 60.8 billion, up 6.9%, and a deficit of $ 10.75 billion.
Brief Table of Trade in Ukraine 2015-2019
(Unit: USD)
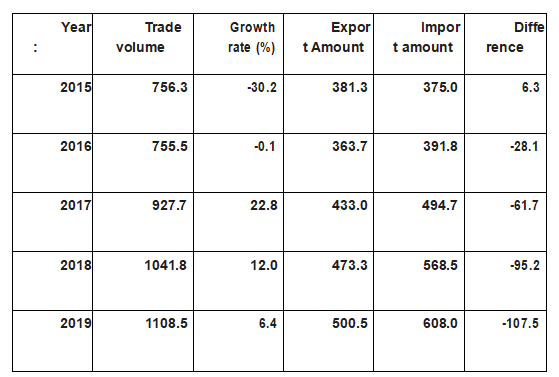
Source: The Ukrainian National Statistics Agency
According to the Ukrainian National Statistics Agency, China became the largest trading partner in Ukraine for the first time in 2019, with the bilateral trade of goods between China and Ukraine reaching US $ 12.79 billion. China is the largest commodity export market in Ukraine, and Ukraine exports USD 3.59 billion, representing 7.2% of total Ukrainian exports; China is also the largest source of imports of Ukraine, importing USD 9.2 billion from China, representing 15.1% of total Ukrainian imports. Ukraine's deficit against China was $ 5.61 billion. By region, the EU is Ukraine 's largest trading partner, with $ 45.75 billion, accounting for 41.3% of Ukraine' s total foreign trade, of which exports were $ 20.75 billion, up 3% year on year and $ 25 billion from the EU, up 7.7% year on year.
Main Ukrainian export markets and sources of imports in 2019
(In: 0 US million)
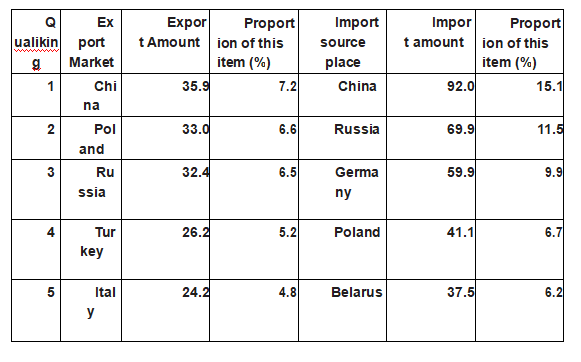
Source: The Ukrainian National Statistics Agency
[Import and Export Commodity Structure] Ukraine's domestic resources and industrial structure determine that the structure of its import and export commodities is relatively single, the export commodities are mainly black metal and food crops, and the imported commodities are mainly oil and natural gas and other energy products. The above structural characteristics determine that its economic development is vulnerable to the international energy and raw material market conditions and its main energy supply countries. In 2019, the major Ukrainian exports and imports are shown in the table below.
Main import and export commodities of Ukraine in 2019
(In: 00 million)
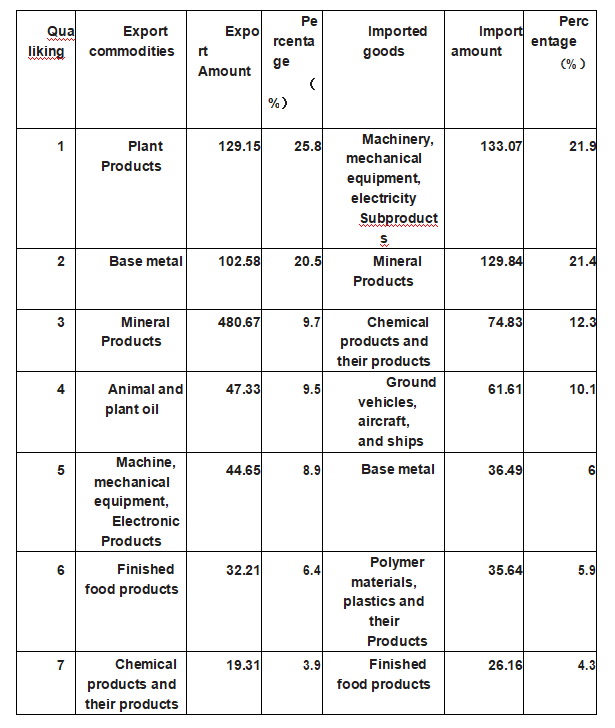
Source: The Ukrainian National Statistics Agency
[Trade in Services] In 2019, the total trade in services totaled $ 21.77 billion, with exports of $ 15.24 billion, up 30.9% year on year, importing $ 6.53 billion, up 3.5% year on year, and a trade surplus of $ 8.71 billion.
Main export markets and sources of imports for service trade in Ukraine in 2019
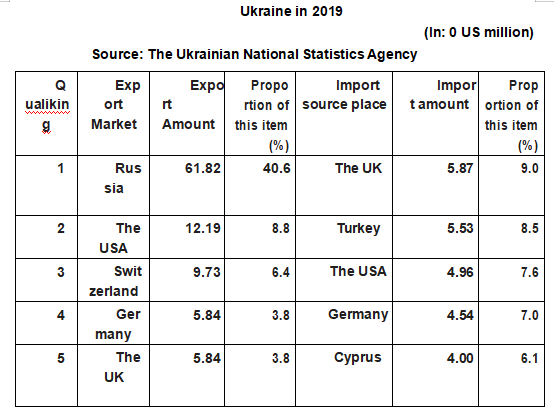
Source: The Ukrainian National Statistics Agency
[Trade in Services Structure] Trade in Services Structure in Ukraine in 2019 is shown in the following table:
Ukraine Trade in Services Structure in 2019
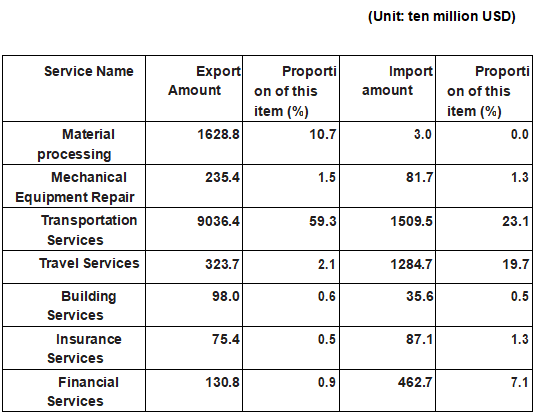
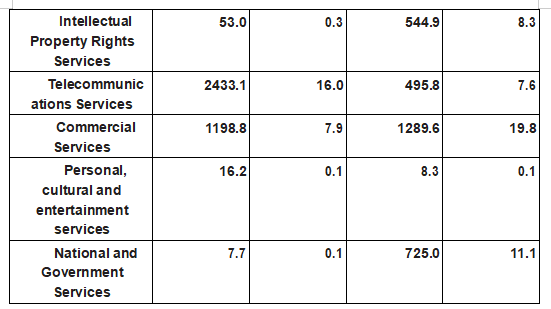
Source: The Ukrainian National Statistics Agency
Since the establishment of diplomatic ties between China and Ukraine, the two countries have signed a series of important government and departmental cooperation agreements in the economic and trade field, mainly including the China-Ukraine intergovernmental Economic and Trade Cooperation Agreement, the China-Ukraine intergovernmental Investment Protection Agreement, the agreement on avoiding double taxation and preventing tax evasion, the People's Bank of China and Ukraine, and the Intellectual Property Protection Agreement between China and Ukraine, which laid the legal foundation for economic and trade cooperation between enterprises between China and Ukraine. In 2019, while implementing the free trade agreement with the EU, Ukraine continued to participate in the construction of "One Belt And One Road", actively attracted Chinese investment, expand China 's exports, bilateral annual trade volume of nearly $ 12 billion, increasing 23.3% year on year, China' s direct investment flow in Ukraine was nearly $ 60 million, both data hit record highs. By the end of 2019, China's direct investment in Ukraine was nearly US $ 150 million, and bilateral economic and technological cooperation in information technology, energy, agriculture and infrastructure was steadily advancing.
According to Chinese customs statistics, in 2019, China-Ukraine trade was USD 11.91 billion, up 23.3% year-on-year, China exports to Ukraine were USD 7.4 billion, up 5.4% year-on-year, and China imported USD 4.51 billion from Ukraine, up year-on-year 70.6%.
In 2020, bilateral trade between China and Ukraine was USD 14.66 billion, up 23.2% year on year, while China exported USD 6.87 billion, decreased 7% year on year, USD 7.79 billion and a year-on-year increase of 72.8%. At present, Ukraine is my third largest trading partner in Eurasia, after Russia and Kazakhstan, and China is Ukraine's largest trading partner.
In 2019, China's exports to Ukraine mainly include motor, electrical, audio and visual equipment and zero accessories, boilers, machinery, appliances and parts, boots, legs, similar products and accessories; plastics and their products; vehicles and zero accessories (except railway vehicles); toys, games or sports products and their parts, furniture, bedding, bedding, spring beds, etc.; steel products; steel; miscellaneous chemical products.
In 2019, the main categories of Chinese imports from Ukraine include: sand, slag and ash; grain, animal and plant grease and its decomposition products; food industry residues and waste preparation; wood and wood products; charcoal; steel; powder industry products; malt; starch; gluten; boiler, machine machinery; motor, electrical, audio-visual equipment and its parts; milk, eggs, honey and other edible animal products.
COFCO Ukraine Nikolyev Wharf

2、 Framework section: the news hotspot
China maintains Ukraine's top trading partner in the first two months of this year
http://ua.mofcom.gov.cn/article/jmxw/202103/20210303046633.shtml
Ukraine conducts trade activities with 234 countries in 2020
http://ua.mofcom.gov.cn/article/jmxw/202103/20210303047287.shtml
Ukrainian major grain exports continued to decrease in this marketing year
http://ua.mofcom.gov.cn/article/jmxw/202103/20210303048499.shtml
Ukraine significantly increased exports of soybean to the EU in April
http://ua.mofcom.gov.cn/article/jmxw/202105/20210503065601.shtml
China is expected to continue to increase import demand for corn in Ukraine in the 2021 / 2022 market year
http://ua.mofcom.gov.cn/article/jmxw/202105/20210503065932.shtml
Experts predict that Ukraine will have a new record of agricultural products export in this marketing year
http://ua.mofcom.gov.cn/article/jmxw/202102/20210203037400.shtml
Ukraine holds German rapeseed market leader, but intensifying competition
http://ua.mofcom.gov.cn/article/jmxw/202102/20210203036722.shtml
3、 Framework section: National · Human Geography
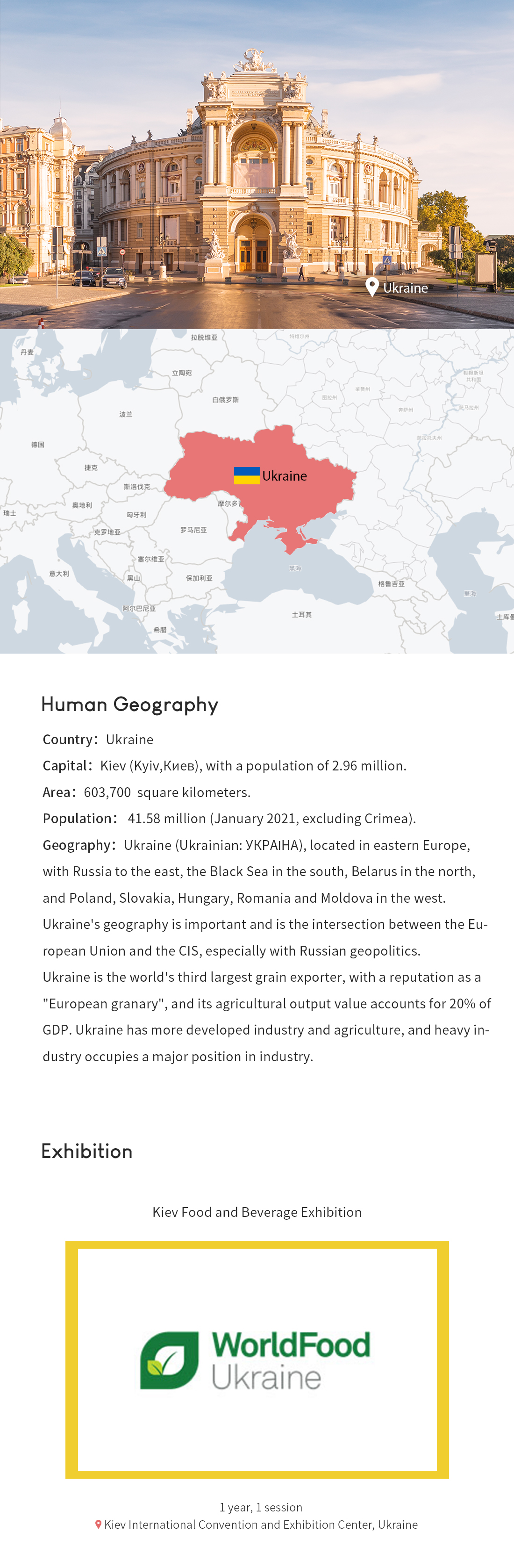
Ukraine (Ukrainian: УКРАІНА; English: Ukraine), located in eastern Europe, with Russia to the east, the Black Sea in the south, Belarus in the north, and Poland, Slovakia, Hungary, Romania and Moldova in the west. Ukraine's geography is important and is the intersection between the European Union and the CIS, especially with Russian geopolitics.
traces of ancient human activity existed in the early Paleolithic territory of Ukraine. The term "Ukraine" was first seen in the Ross Records (1187), meaning "frontier". In 1240, the Mongol Imperial Expeditionary Force (Batu) occupied Kiev. Later the Mongol Golden Khanate, the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and Poland ruled Ukraine. In 1654, the Ukrainian Cossack leader signed the Pelyaslav Contract with the Russian tsar, and Ukraine and Russia were formally merged. Since then, Ukraine has had its own government, but it has not played a substantial role. Joining the Soviet Union in 1922 (Western Ukraine joined in 1939). On 16 July 1990, the Supreme Soviet of Ukraine adopted the Declaration of the National Sovereignty of Ukraine. Then on August 24,1991, Ukraine declared its independence.
Ukraine is the world's third largest grain exporter, with a reputation as a "European granary", and its agricultural output value accounts for 20% of GDP. Ukraine has more developed industry and agriculture, and heavy industry occupies a major position in industry. [1] On 25 November 2018, the Ukrainian armed forces entered full combat readiness under the orders of the Chief of the General Staff.
On 5 September 2019, the Ukrainian Supreme Anti-corruption Court was established. The task of the Supreme Court on Anti-Corruption is to punish corrupt officials and protect the rights and interests of the state, society and investors.
Ukrainian Landscape Introduction: https://v.qq.com/x/page/l0810zhxy4i.html? ptag=qqbrowser
Ukrainian scenery: https://v.qq.com/x/page/a0502gwfhha.html? ptag=qqbrowser
4、 Frame Section: Latest Information
Prices rise Ukrainian oil exports rose 33%
http://ua.mofcom.gov.cn/article/jmxw/202103/20210303046628.shtml
Ukrainian grain exports have reached 34.07 million tons in the past marketing year
http://ua.mofcom.gov.cn/article/jmxw/202103/20210303046631.shtml
Ukraine exported 95,000 tons of flour in the 2020 / 21 market year
http://ua.mofcom.gov.cn/article/jmxw/202103/20210303048497.shtml
Experts forecast 40% reduction in Ukrainian soybean meal exports in 2020-2021 market
http://ua.mofcom.gov.cn/article/jmxw/202102/20210203036724.shtml
Total import of Ukrainian imports in 2020 $ 841 million
http://ua.mofcom.gov.cn/article/jmxw/202102/20210203036726.shtml
Ukrainian agricultural exports fell in January 2021
http://ua.mofcom.gov.cn/article/jmxw/202102/20210203037401.shtml
Ukrainian Retail Trade turnover is up 8.4% in 2020
http://ua.mofcom.gov.cn/article/jmxw/202101/20210103034238.shtml
Ukrainian fish exports in 202013%http://ua.mofcom.gov.cn/article/jmxw/202101/20210103034240.shtml
Ukrainian fruit berry exports fell by 8% in 2020
http://ua.mofcom.gov.cn/article/jmxw/202101/20210103035432.shtml
Ukrainian grain exports have reached 28.74 million tons in this marketing year
http://ua.mofcom.gov.cn/article/jmxw/202102/20210203036723.shtml
II. Professional framework section
5, Framework Section: National · Food Introduction
[Agriculture] Ukraine is rich in arable land resources, with 41.5 million hectares of agricultural land, accounting for 70% of the land area. The soil is fertile, black soil area of 24.898600 hectares, 60-80 cm, humus content, 4.7% -6.1%, the soil solution reaction is neutral and the bottom of the section is weak alkaline. Water sufficient water resources, convenient irrigation, suitable for agricultural production. Ukraine's main crops include grain grain, oil crops, sugar crops, and potatoes. Over the years, Ukraine has achieved crop output on an average of 1.5-2 times its domestic demand, and exports exports to the EU, Asia and North Africa. At present, Ukraine has been the world's largest exporter of sunflower oil and sunflower meal exporter, the third largest grain exporter, the third largest rapeseed and walnut exporter, the fourth largest exporter of barley and corn, and the sixth largest exporter of soybean. Sugar products also have an significant share in the European market. In 2019, Ukrainian agricultural output was 409.3 billion Grivna, up 3.8% year on year, and grain and grain beans were 75.143 million tons, up 7.3%. In the 2018 / 19 marketing year, exports of Ukrainian grain, edible beans and flour broke a record of 50.4 million tonnes, a 23% year-on-year increase. As of April 22,2020, Ukrainian grain export in the 2019-2020 marketing year was 4 8.950 million tons, up 8.25 million tons, including wheat export of 18.55 million tons, 25.2 million tons of corn, 4.55 million tons of barley and 290,200 tons of flour.
Animal husbandry accounts for about 30% of Ukraine's agricultural output value, but the development is relatively low. After the government cancelled financial subsidies for the industry, production costs increased and interest rates were reduced. Feed crops account for only 7.1% of the cultivated area. The cattle stock has fallen 85.7% over the past 10 years and 75% of the cows are raised by farmers. Seventy-four percent of the sheep are raised by farmers, and the industry has lost more than 70 percent in the past 10 years.
The main bottleneck of Ukraine's agricultural development is: low cultivated land utilization rate, compound index is only 0.6; insufficient deep processing capacity, export mainly raw materials, low added value; warehousing and logistics infrastructure backward to guarantee export capacity; agricultural enterprises difficult to obtain credit and insufficient capital investment.
6、 Framework section: Food Standards
Ukrainian food safety will adopt EU standards
On 19 September, 2015, according to the Ukrainian news agency, under the act on the revision of food legislation on parts of Ukraine (№ 4179), most of the provisions relating to EU integration came into effect on September 20th. The law aims to align Ukrainian legislation in the field of food safety and quality with EU legislation.
The new law stipulates the introduction of a European model of food safety and quality system based on the "field to dining table" principle and HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Key Control Points) procedures in Ukraine. Without the corresponding laws, Ukraine will be unable to implement the food supply quotas within the framework of signing the EU contact agreement. The new law significantly reduces the number of administrative control procedures and national regulation, eliminating licensing procedures that are not available in the EU. Detailed requirements for the national regulatory procedures in the Ukrainian markets are defined in accordance with the EU practice. This will apply only to businesses engaged in the animal source food production and / or storage business. For other enterprises, including public catering places and some retail places, complete the registration procedures.
Under the new law, food safety supervision will be supervised by a state authority. The entire food production chain will be under supervision. Enterprises need to grasp the source of raw materials or food, the accurate information of the enterprise delivery direction.The above information must be kept for 6 months after the marked food sale deadline. Heavy penalties are imposed for the failure to comply with food legislation. An effective accountability system shall be implemented for producers, other market operators (within their business scope) and regulatory agencies that violate the standards of the Food Safety Law.
With the time and certain resources required to introduce HACCP, the Act contains special provisions that come into effect 2-5 years from the date of publication. Among them, Part 7 of the —— food processing general hygiene requirements will take effect on September 20,2016. This section requires market operators to ensure the health and cleanliness of plants and animals that have an impact on people's health. Chapter 20, paragraph 2 [for Enterprises (except small businesses) of raw ingredients (except small businesses)] and Chapter 64, paragraph 4 [for small businesses], September 20,2017, September 20,2018 and September 20,2019. Chapter 36 Section 1 [Sales of Household Products on the basis of the certified laboratory results in the agricultural market] will take effect on September 20,2019.
It is reported that the law on Amendment to Part of Ukraine was passed by Parliament on 22 July 2014 and published in the "Voice of Ukraine" on 19 September 2014.
HACCP is the system of hazard analysis and key control points adopted by international organizations. The HACCP system transforms it from final product testing to developing precautions. To implement the HACCP system, manufacturers need to check not only their own products and their manufacturing methods, but also to raw materials and accessories suppliers, distribution and retail systems.
At present, Ukraine implements the national standard DSTU4161-203《 food safety management system. Requirements (since 1 July 2003) and national standard DSTUISO22000:2007 (as ISO22000:2005. Since August 1,2007)
7、 Framework Section: Policy and Regulations
7.1 What are the regulations and policies on foreign trade?
7.1.1 Trade Authority
The Ukrainian Ministry of Economic Development, Trade and Agriculture is the national industry competent department of foreign economic and trade, responsible for formulating and implementing foreign trade policies and coordinating relations with various departments on specific policies.
At the end of 2018, the Ukrainian government launched the reform of the fiscal and taxation system, dividing the State Finance and Taxation Administration into the State Taxation Administration and the State Customs Administration. On 28 August 2019, the State Taxation Service was officially operational. The functions of the department include other regulatory issues such as implementing national tax policies, compulsory unified collection and management policies of national social insurance, and cracking down on violations of the tax law and the unified social fee law. On 8 December 2019, the Ukrainian Customs Service started operation.
7.1.2 Trade Regulatory System
In 1992, Ukraine formulated the first Law on Foreign Economic Activities after independence, which established the reform and development direction of the foreign trade management system: the liberalization of foreign trade and the integration into the world trade system. The law stipulates that the registration system of the management right of foreign trade is implemented, that is, all legally registered enterprises in Ukraine shall automatically obtain the management right of foreign trade after applying to the Ministry of Ukraine for the relevant registration procedures of Economy.
Currently, Ukrainian laws on trade and investment, in addition to the Foreign Economic Activities Law, mainly include the Ukrainian Customs Law promulgated in 2004 and the Foreign Investment System Law promulgated and implemented in 1996 and amended in 2000. Relevant legal text can be found in the legal text column on the Ukrainian parliament's website.
Website: zakon1.rada.gov.ua/cgi-bin/laws/main.cgi
Relevant Provisions for 7.1.3 Trade Management
[Import and Export Quota and License System] Ukraine controls license quotas for import and export commodities amid a sharp trade deficit, an imbalance between supply and demand, and a trade discrimination against other countries.
The Government of Ukraine shall publish the list of commodities for active import and export quotas every year, the Ministry of Economy and Trade and its subordinate authorized departments shall work with the relevant departments of the government to issue certificates and supervise the use, and the Customs shall release the number of commodities with the strength of relevant documents. The list and duration of goods subject to quota license management also need to be approved by the Ukrainian parliament. Currently, import quotas (implemented through non-automatic licenses) are only used to provide safeguards for specific seamless steel pipes.
7.1.4 Import Commodity Inspection and Quarantine
According to the relevant regulations of Ukraine, the categories 1-24 commodities in the catalogue of international trade goods must be provided with the quality certificate of the goods and the foreign quality certificate when entering the customs customs of Ukraine. Ukraine's body in charge of the quality inspection of imported goods is the National Standards and Measurement Certification Committee of Ukraine. The Ukrainian National Standards and Measurement Accreditation Committee and 25 standards certification centers in the states are responsible for the inspection and certification of imported goods.
The Food Safety and Consumer Protection Department of Rights and Interests of Ukraine is guided by the Ministry of Economics and Trade, and is responsible for formulating the quarantine catalogue, procedures and standards of import and export commodities according to the characteristics of animal and plant epidemics, and implementing the inspection and laboratory functions. It is the competent department responsible for the quarantine of import and export commodities.
[Import Commodity Inspection Procedure]
(1) Mandates certified merchandise. According to the Ukrainian Certification Standards Regulations, more than 100 imported goods must be certified before they can enter Ukraine and sell, such as telephone program control switches, drugs, toys, agricultural products, food raw materials, etc. Gifts, exhibits, humanitarian aid and technical aid goods, input in means of production under enterprise legal funds, foreign materials, customs bonded goods and transit goods are exempted from compulsory certification.
In 2015, Ukraine cancelled the mandatory certification of low-risk life and health products that meet EU standards. The first batch of deregulation commodities were agricultural machinery and food.
(2) non-mandatory certified merchandise. As long as the commodity inspection certificate of the commodity producer country, and in the sampling inspection can import, sell, such as some daily light industrial products and food, some raw material products, etc. Ukraine conducts separate certification of technical equipment products.
(3) mutual free certified goods. According to the bilateral cooperation agreement signed by Ukraine, if the agreement, the commodity can be exempted from the quality certification procedures when entering Ukraine.
[Inspection Standards for Imported Commodities] According to Ukrainian regulations, goods imported from abroad should be inspected according to relevant standards.
(1) For similar domestic products in Ukraine, corresponding standards of domestic technology, pharmacology, health, plant hygiene, veterinary and ecological verification standards are adopted for imported products.
If (2) does not produce similar commodities in Ukraine, the incoming (outbound) manufacturer shall provide product quality certificates meeting current international technical, pharmacological, sanitary, sanitary, veterinary and ecological standards, or the national standards of the major exporting countries of the commodity.
(3) Where Ukraine and the corresponding countries sign an agreement to mutually recognize the results of the commercial inspection, the importer shall present the proof that the product meets the current standards in the exporting country.
In 2015, the Ukrainian government cancelled the mandatory health epidemic test.
7.1.5 Customs Management Rules and Regulations
[Customs Duty System] Ukrainian customs tariffs are based on internationally recognized standards and develop in the direction of being in line with the principles and rules of customs affairs recognized in international practice. The tariff rate is submitted to the Ukrainian parliament for approval, with consistency with all subjects of foreign economic activities, unless otherwise stipulated by relevant laws and international treaties.
[Tariff Rate] After Ukraine joined May WTO, 2008, import tariff rates are on the parliamentary website (website: portal.rada.gov. ua) was announced. Ukraine is bound by the tariff rules, and according to the Ukrainian Ministry of Economy, the average Ukrainian tariff level has now fallen to 6.1%, with the average industrial tariffs falling to 4.9% and agricultural products falling to
10.8%. In addition, according to the signed tariff agreement on classified goods signed, some of the individual products, such as chemicals, wood, textiles, drugs, furniture and other import tariffs are zero.
The MFN(Favourite) rate used in Ukraine is slightly below the average rate above, at 9.6% (agricultural products) and 3.6% (industrial products) respectively. In industrial products, MFN tariff average items of over 10% are limited to clothing, shoes and socks, various accessories, and suitcase bags. MFN ad valorem tax rates for any item will not exceed 20%, but sugar (50%) and sunflower oil
(30%) Except. The import of raw sucrose is subject by MFN tariff quota, only 267,800 tons per year. However, over the past four years, Ukrainian sugar imports are negligible.
China is included in the preferential tariff rate (50%). Chinese commodities can enjoy preferential tariffs: goods imported directly from China; producers are enterprises registered in China; and issue FORM-A certificate of origin.
The Ukrainian customs import duties are a differential tax. In terms of type of goods, zero tariff for goods dependent on import; 2% -5% on goods with insufficient production capacity; over 10% for goods with large output and substantially satisfying demand; high tariff for goods with high output and export needs. From the perspective of commodity sources, goods from countries and regions that have signed customs agreements and international agreements with Ukraine impose special preferential tariffs or even import tariffs according to the specific terms of the agreement. Full general import tariffs will be imposed on goods from countries and regions that have not yet signed free trade agreements or preferential economic and trade agreements with Ukraine, or goods from the specific source country of origin cannot be determined.
[Tariff Collection] Generally adopts the following methods (see Article 57 of the Customs Law): (1) ad valorem tax. That is, the import and export goods and goods according to a certain percentage of the customs value. (2) derived from the volume tax. That is, certain customs duties are levied on import and export goods and goods. (3) Mixed Tax. That is, customs tariffs are levied on the import and export commodities and the above two ways of mixing the commodities and goods.
Besides beer, wine, and some tobacco products, the Ukrainian customs office has mostly adopted the ad valorem tariff calculation method (also known as the percentage method). The quantitative tariff calculation method is usually only for imported goods that impose special tariff rates as stipulated by Ukrainian law, such as guns for hunting and other weapons with gun barrels. Ukrainian customs used mixed tariff calculations. The Ukrainian customs has adopted the hybrid tariff calculation method for automobile import, that is, levied a certain percentage tariff according to the customs value, but the exhaust volume shall not be less than a certain amount, and then revised to a unified automobile import tariff rate of 20%, reduced to 10% after entry, and the import tariff rate of automobile bulk parts is 5%.
The tax base of import tariffs of Ukrainian customs is the customs value of imported goods. Article 15 of the Ukrainian Uniform Tariff Rate Law stipulates that the customs value of import goods includes: the price of goods indicated on the waybill, shipping fees, packing fees, unloading fees, and transportation to the customs border of Ukraine; sales fees and intermediary fees; royalties for intellectual property and patent rights. In addition, all imported goods are subject to 20% VAT on import and certain goods.
[Tariff Category] Ukrainian customs duties include the following types (see Article 271-275 of the Ukrainian Customs Law): import duties; export duties; seasonal duties; special forms of duties, including special duties, anti-dumping duties and compensatory duties.
No other type of tariff shall be imposed except the contents specified in the Ukrainian Customs Act.
[Import duties] Duty imposed on imported goods. Tariff rates are determined in accordance with the Customs Tariff Act of Ukraine and the amendments are implemented with the approval of Parliament.
Since 1 January 2016, Ukraine has imposed zero tariffs on all vehicles installed with electric motors. Such vehicles include electric motor vehicles, equipped with bicycles and trolleybuses with a rated output power of no more than 250 watts of auxiliary electric motors.
[Export duties] Duty imposed on outbound goods. As part of its accession clause, Ukraine worked to reduce its tariffs on exports of live livestock, canola, raw skin and scrap metals. Since 2008, export tariffs have been levied for natural gas produced in Ukraine and exported in liquefied or gaseous form. However, the Government has lifted the export tariff from EEC members in 2014. In the second half of 2011, temporary export tariffs on specific grains began. A 10-year ban was applied to raw timber from 1 November 2015. The injunction has applied to pine logs since January 1,2017.
Ukraine will terminate its export tariffs on the EU trade from 2024 from 1 January 2024.
[Seasonal duties] A duty imposed on parts of the goods under the law. Seasonal duties shall be calculated from the date of publication, and the collection period shall not be less than 60 days or more than 120 calendar days.
[Special forms of tariff] To protect the economic interests of Ukrainian and Ukrainian producers, other special forms of tariffs may be imposed on imported goods. Such duties are levied separately and are not subject to other duties. The current special forms of tariffs levied in Ukraine mainly include the following: special tariffs, anti-dumping duties, and compensation tariffs.
(1) Special Tariff: Use is to protect the interests of domestic commodity producers when the quantity of imported goods and their import conditions may cause threat or significant damage to the production of their own goods, and to counter them when other countries, customs alliances or economic groups adopt discriminatory policies and / or unfriendly practices against the rights and interests of foreign trade operators in Ukraine.
Collection and details of special tariffs in recent years:
(2) Anti-dumping Tariff: According to Ukraine on the Protection of Domestic Commodities Producer from Import
The contents of the Dumping Damage Act shall establish anti-dumping duties. Anti-dumping duties are used when imports have dumping facts and may cause loss or damage to national production.
From 29 December 2014 to 29 December 2019, Ukraine imposed a 41.07% antidumping tax on seamless stainless steel pipes imported from China for 5 years, 2019.
From April 17,2019, Ukraine imposed an 8.45% anti-dumping tax on medical rubber plugs imported from China for five years.
(3) Compensation Tariff: According to the Ukrainian Law on the Protection of Domestic Commodity Producers from Import Subsidies, import goods are the object of import subsidies, and use compensation tariffs when the subsidy may constitute damage to domestic producers.
(4) legal basis for the use of special forms of tariffs (see Article 275 of the Ukrainian Customs Act): Special form duties are formulated by the Inter-sectoral Committee of Ukraine under the Ukraine Law on the Protection of Domestic Commodity Producers (Antidumping Law), the Ukraine Law on the Protection of Domestic Commodity Producers from Import Subsidy Injury (Countervailing Law) and the Ukraine Law on Special Measures for Import Trade.
If the imports are the subject of special measures, anti-dumping or compensation measures, they will be denied, suspended or suspended with the approval of the Ukrainian parliament (see Article 281, paragraph 5, of the Ukrainian Customs Act).
(5) Current special forms of tariffs in Ukraine also include:
Import additional tax: cancel additional tax from January 1,2016. Ukraine began collecting a 13% additional import tax on specific goods in March 2009. The tax fee was cancelled in May and September 2009. The WTO Balance of payments (BOP) restriction Committee felt that the BOP situation in Ukraine was not suitable for taxation measures and the move did not comply with WTO regulations.
War Tax: levied since 3 August 2014 at 1.5% for all income residents, income non-residents in Ukraine and other taxable agencies. As of 8 May 2020, war taxes entered 7.781 billion Griffner.
[Customs Appraisal System] The Ukraine Customs Law has detailed the customs valuation and valuation method, and refer to Article 49-66 of Chapter III of Ukraine Customs Law. The Ukrainian customs generally conduct the customs price estimation in the following 6 ways (see Article 57 of the Customs Law): (1) evaluates the actual transaction price of the imported goods; (2) evaluates the price of the same commodity;
(3) is valued at the price of similar commodities; (4) decreases at the transaction price of similar commodity market; (5) increases at the transaction price of similar commodity market; (6) Other methods.
At present, the first valuation method is more used by Ukrainian customs, but valuation disputes often occur between import enterprises and customs.
7.1.6 export tariffs and export restrictions
Ukraine is exempt from livestock and fur products, non-ferrous metals, scrap metals and special equipment, from export commodities, including export management commodities. For products restricting export, the following two categories mainly include:
[Restricted Export Products] Ukraine actively restricts the export and the export of other finished products restricted by the import of the economic organizations or the economic organizations of the customs union, shall be conducted in accordance with the Ukrainian government regulations and under the authorization of the Ministry of Economy.
[Export control of weapons and dual-use products] Ukraine conducts national export control on the transfer of weapons, military and special technologies, and the production of raw materials, equipment and crafts. Enterprises operating state export control commodities shall need to apply to the government for the special right of management. The export contracts for controlled commodities shall only be implemented after the approval, issuance and registration of the Special Export Supervision Bureau of the Ministry of Economy, and the Customs shall inspect and release the contracts with the license. List of export-controlled goods is determined by the Government of Ukraine. State-controlled commodities include weapons, ammunition, military technology and their production sets of equipment, explosives, nuclear materials, nuclear technology, nuclear equipment, nuclear devices, special non-nuclear materials, ionizing radiation sources; other products, technologies and services used for military equipment and military technology and constitute state secrets of Ukraine; precious metals, alloys, gems, narcotics, works of art, museum collections, etc.
[No Export] On 19 April 2015, Ukraine issued a law to suspend log export for 10 years. No pine exports are enforced on January 1,2017, and tree species other than pine trees began on November 1,2015. In addition, oak is listed on the list of precious and rare tree species. In September 2018, the ban on wage material exports was lifted.
[List of goods embargo against Russia] The list of goods between Russia to Ukraine took effect on January 10,2016. The embargo continued until 5 August 2016 or the cancellation of the Russian embargo on agricultural products like food and raw materials of origin in Ukraine. List of Russian goods prohibited from Ukraine include beef, poultry meat and chicken (fresh meat, chilled and frozen), edible animal offails, pickled food, fish and shellfish, dairy products, soft cheese, coffee, tea, mixed additives, sweets, candy and baked goods, potatoes, children's food, macaroni, sauces, spices and seasonings, beer, alcoholic drinks, vodka, cat and dog food, cigarettes, shower gel, pesticides, antibiotics, herbicides, rodents, trains and tram equipment, diesel motor locomotives.
The Ukrainian government has approved the implementation of the import tax rate of 0.5% -10% on Russian goods since 2 January 2016. On 1 January 2016, Russia imposed an embargo on Ukrainian goods, with the execution period running until 5 August 2016. In 2017, the Ukrainian government decided to extend the embargo until August 2018. Meanwhile, it was approved to ban the import of Russian chemical fertilizer. In December 2018, Ukraine announced that it would extend an embargo on some of the Russian goods and an import tax on other goods against Russian trade sanctions in 2016 until 31 December 2019. In December 2019, the Ukrainian cabinet decided to extend the special tariff policy on imports from Russia until 31 December 2020. As of May 2019, the Ukrainian government has repeatedly expanded the embargo list of goods imported from Russia. Forbidden goods include starch, glucose, van springs, canning boxes, food bottles, voltage conductors, cement, plywood, and similar laminate materials, etc.
7.1.7 Commodity Certificate of Origin
[Standard for issuing commodity certificate of origin] is as follows: the added value of (1) products processed in Ukraine reaches more than 50%; the customs tax number of (2) products processed in Ukraine has changed.
[Issuing Agency] The certificate of origin in Ukraine is the Ukrainian Chamber of Industry and its branches.
[Documents required for the certificate of origin] Ukrainian enterprises and foreign investment enterprises registered in Ukraine have the right to apply for a certificate of origin. The necessary documents for obtaining a certificate of origin include:
(1) Enterprise files;
(2) product production or sales contract;
(3) commodity Shipping order;
(4) payment voucher;
(5) Product Quality Certificate;
Use instructions of (6) technical equipment products;
(7) Application for issuance.
[Foreign Trade Contract Registration System] According to the regulations, where the Ukrainian export commodities, active export reduction in order to prevent foreign anti-dumping investigation, and Ukrainian export commodities under foreign anti-dumping investigation, the export contracts must be registered. The list of commodities that implement the export contract registration system shall be determined by the Ministry of Economics and Trade of Ukraine.
[Guiding Price] Ukrainian Ministry of Economy and Trade regulates the commodities subject to anti-dumping sanctions and anti-dumping investigation inside and abroad Ukraine and the use of national foreign exchange funds to purchase complete sets of equipment or commodities imported through international bidding.
[Special Sanctions] The laws of Ukraine may impose special sanctions on domestic and foreign enterprises under the following cases: enterprises that violate the Ukrainian laws concerning anti-monopoly measures, prohibiting unfair competition, restricting transfer and dumping, and suspend the management of foreign trade in violation of relevant Ukrainian laws and engage in activities that may endanger the national economic security. Special sanctions are implemented by the Ministry of Economy and Trade of Ukraine based on the ruling of the judicial organs.
7.2 Relevant Legal Consultation Business Office of the Ministry of Commerce in Ukraine and the website of the Ministry of Commerce:
7.2.1 Foreign Trade Policy
http://ua.mofcom.gov.cn/article/g/200311/20031100150903.shtml
7.2.2 Uniform Tariff Law
http://ua.mofcom.gov.cn/article/g/200311/20031100151437.shtml
7.2.3 Ukraine Import Guarantee Measures Implementation Law
http://ua.mofcom.gov.cn/article/g/200311/20031100151491.shtml
7.2.4 Ukraine Import and Export Management Related Policy
http://ua.mofcom.gov.cn/article/g/201201/20120107922225.shtml
7.2.5 Ukrainian Investment Law (English, Russian)
http://ua.mofcom.gov.cn/article/g/201303/20130300072918.shtml
8、 Frame section: Exhibition Exhibition (Food)
Kiev Food and Beverage Exhibition
Exhibition data
Exhibition scale: 15,000 square meters
Professional audience: 11,251 people
exhibitors: 288
Host cycle: 1 year, 1 session
Exhibition introduction
Kiev Food and Beverage ExportThe Kiev Food and Beverage Exhibition (World Food Ukraine) is the largest and most extensive food and beverage exhibition in Ukraine. Founded in 1998, it is hosted by the globally renowned UK ITEGroupPLC.. The exhibition covers all categories of the food and beverage industry. It is a platform that independently connects high-quality trade buyers and influential trade industry insiders with individual exhibitors, regional exhibitors and national exhibitions. It is an international event in the food field of Ukraine.
The food and beverage market is in fast development, growing consumer income and the diversity of consumer choices, Ukraine Kiev Food and Beverage Show World Food Ukraine offers good business opportunities for suppliers at home and abroad.
The four major features of the Ukrainian food industry are the rapid increase in supermarkets and convenience stores; consumers are also seeking more diverse products, urban consumers also need more convenience products, and consumers demand better quality, healthier and more environmentally friendly products. Kiev Food and Beverage Exhibition, Ukraine World Food Ukraine is undoubtedly an excellent opportunity for Chinese companies to develop the market, establish trade links, and obtain the latest developments in the local food industry.
Exhibit exhibits
Food additives, food ingredients, beverages (alcohol & soft drinks), etc
Food production of raw materials, additives, condiments, etc.
Frozen food & canned food & semi-finished products, etc
Food processing machinery, food packaging machinery, grain screening, processing, transportation and storage, etc.
Frozen & sales equipment, retail, supermarket equipment, etc
Health food, etc.
Kiev International Convention and Exhibition Center, Ukraine
Pavilion Address: Brovarskiy Avenue 15,Kiev,Ukraine,02000
9、 Framework section: Food category
Agricultural products, food, oil products, vegetables and fruits, sugar beets, milk, meat, and eggs.
10、 Framework section: Brand recommendation
НАК "Нафтогаз Украіни"
ДП "Енергоринок"
ПрАТ "Арселор Міттал Кривии Ріг"
ТОВ "АТБ-Маркет"
ТОВ "Тедіс Украіна"
Nibulon
11、 Framework plate: Corporate recommendation
Ukraine's agricultural market is highly open. Large international institutional investment is active. Major agricultural enterprises are: (1) Ukrlandfarming, owns 654,000 hectares of land; (2) NCH Agro, owns 430,000 hectares of land; (3) Kernel, owns 390,000 hectares; (4) MHP, has 360,000 hectares, and (5) Mriya, owns 259,000 hectares.
12、 Framework section: National · Food Data
Ukraine is rich in grain and has a reputation as a "European granary". In recent years, Ukraine has had a bumper grain harvest year after year, producing more than 70 million tons and exporting over 40 million tons, making it is the world's third largest grain exporter and the largest exporter of sunflower oil. In 2013, Ukraine produced 62.3 million tons, ranking 8th in the world. Grain exports of 26.8 million tons, accounting for 43% of the total Ukrainian grain output and 10% of the global grain exports, is the world's fifth largest grain exporter. Major export destinations are Spain, the Middle East and North African countries. In the first nine months of 2014, Ukraine ' food exports to China totaled $ 154 million.
In 2013, Ukrainian oil crops produced 17.6 million tons, ranking 8th in the world. Among them, 11 million tons, ranked first in the world, accounting for 27% of the global output. Current export tariffs are 10% and 99% of sunflower seeds are processed in Ukraine. The export volume of sunflower oil is 3.2 million tons, accounting for 89% of the total output of sunflower oil, ranking the first in the world, accounting for 53% of the total global exports. The export volume of oil crops is 3.9 million tons. Ukrainian sunflower oil was mainly exported to China, India and Egypt, with the total sunflower oil to China totaled $ 403 million in the first 9 months of 2014.
In 2013, the milk production of Ukraine was 11.5 million tons, including 23% from enterprise production; 2.4 million tons, 60% from enterprise production; eggs were 19.1 billion, including 63% from enterprise production. Sugar yields of 1.2 million tonnes (normal annual yields of 2 million tons). Ukrainian exports of livestock products and sugar are restricted not only by trade barriers in importing countries, but also by the price of Ukrainian products (sugar, pork) and quality (milk, beef). For example, the construction of modern dairy farms, dairy products including baby milk powder can fully meet foreign needs after certification.
In 2016, Ukrainian agricultural and food exporters exported $ 4.2 billion to EU countries, a 1.6% increase from 2015. The main exports are grains, sunflower oil, oilseeds, fruit and nuts, honey, meat, candy and fruit juice. "We see growth in exports of major commodities leading to overall agricultural exports, such as $ 505 million in sunflower oil ——, $ 36.1 million and $ 16.5 million in sugar ——," said Trofimzeeva, Deputy Minister of Agriculture for European Integration. In 2016, exports of partially fresh or processed foods increased significantly. canned tomatoes doubled, cucumber-1.7 times, fresh fruit-1.5 times, margarine-8 times. "For us, this means the diversification of export results and is a positive trend."
In 2016, after Asia (45.9%), Europe was the second largest export destination of Ukrainian agriculture and food, representing 27.5 per cent. Last year, EU agricultural trade was 31.5%. The top five EU importers are Spain, Poland, the Netherlands, Italy, and Germany. According to the Ministry of Agriculture, the trade surplus of agricultural products with Europe was $ 2.3 billion, and the trade turnover with EU countries was $ 6.2 billion. The main trading partners are Spain (15.3%), Poland (14.3%), the Netherlands (14%), Italy (12.6%), Germany (10.1%), Finland (8.4%), Belgium (3.2%), the United Kingdom (3%), Portugal (2.7%), Romania (2.2%), Greece (2%), Hungary (2%).
13、 Chinese Embassy (Consulate) in Ukraine
The Chinese Embassy in Ukraine
Ambassador: Fan (Fan Xianrong)
Address: 32 Grushevsky Street, Kiev City
NO.32,GRUSHEVSKOGO STR.,KYIV,UKRAINE,01901
Postal 01901
National Area Number: 0038-044
Office: 2533154,2531049
External Group: 2533492
Fax: 2302622,2537371
Website: http://ua.chineseembassy.org
http://ua.china-embassy.org
Email: chinaemb_ua@mfa.gov.cn
Business Office of the Chinese Embassy in Ukraine
Address: lane Zemljansky 11,Kyiv,Ukraine
Postal 01014
Tel: 0038-044-2847710 Fax: 0038-044-2848040
Email: ua@mofcom.gov.cn Website: ua.mofcom.gov.cn
Consulate General in Odessa (Ukraine)
Consul-General: Song Liqun)
Address: # 2, Nasimov Hutong, Odessa, Ukraine
Lane Nakhimova 2,Odessa,Ukraine,65014
Postal code: 65014
Tel: 0038-048-7871898,7994217
Fax: 0038-048-7373031,7293250
Website: http://odessa.chineseconsulate.org/
Business Consul of the Chinese Consulate General in Odessa
Address: Lane Nakhimova 2,Odessa,Ukraine
Postal code: 65014
Tel: 0038-048-7173238
Fax: 0038-048-7373031
- Ukrainian Embassy (Consulate) in China
The Ukrainian Embassy in China
Embassy of Ukraine
Office: No. 11, East Sixth Street, Sanlitun, 100600
Chancery: No. 11, Dong Liu Jie, San Li Tun
Tel (Tel): 65326359 (Communication) 65326314 (Trade) 65326821 (Officer) 65326783 (Consul)
Fax (Fax): 65326765 65324014 (Consular)
Email (E-mail):emb_cn@mfa.gov.ua
Website (Website):www.mfa.gov.ua/china, china.mfa.gov.ua/zh
The Consulate-General of Ukraine in Guangzhou
Consulate General of Ukraine in Guangzhou
Office: Room 1407, CITIC Plaza, No. 233, Tianhe North Road, Guangzhou, Guangdong, 510613
CHANCERY:Room1407,CITIC Plaza,233 Tianhe Bei Road,Guangzhou,Guangdong Province
Tel. (TEL): 020-38773755,020-38773550
Fax, FAX: 020-38773513
Website: guangzhou.mfa.gov.ua
Area: Guangdong, Guangxi, Hainan, Hunan, Guizhou
DISTRICT:Guangdong,Guangxi,Hainan,Hunan,Guizhou
The Ukrainian Consulate-General in Shanghai
Consulate General of Ukraine in Shanghai
Office: Room 402, West Tower, Sun Square, 88 Xianxia Road, Shanghai, 200336
CHANCERY: Room 402,West Tower Sun Plaza,88 Xianxia Road,Shanghai
Tel. (TEL): 021-62953195
Fax, FAX: 021-62953171
Email: gc_cns@mfa.gov.ua
Website: shanghai.mfa.gov.ua/zh
Area: Shanghai, Zhejiang, Jiangsu, Anhui, Fujian, Jiangxi
DISTRICT:Shanghai,Zhejiang,Jiangsu,Anhui,Fujian,Jiangxi
- Economic and Trade Organization (Business Association)
Ukrainian Chamber of Industry
Address: 33, Velyka Zhytomyrska Str.,Kyiv
Postal 01601
Tel: 0038-044-5842824 Fax: 0038-044-5842827
Email: ucci@ucci.org.ua Website: www.ucci.org.ua
Investment Promotion Bureau under the Government of Ukraine Website: ukraineinvest.com/
Appendix List of Ukrainian Chinese Enterprises Chamber of Commerce, Chinese Societies and Major Chinese Enterprises
(1) Ukraine China Chamber of Commerce Website: www.cca.com. ua
Address: str Sretenskaya 10,Kyiv
Tel: 0038-073-1540772
Ukrainian China Chamber of Commerce
In order to unite with Ukraine market winter, deep participation in Ukraine business environment improvement process, and provide service platform for future trade and investment cooperation, on the basis of voluntary participation, five Chinese companies (Lenovo Ukraine company, Huawei technology Ukraine, Ukraine company, China complete set Ukraine co., LTD., Eco-Vtor company, Sany Ukraine company) as the sponsor signed Ukraine China chamber of commerce on May 18,2015. On 7 September 2015, the Ukrainian China Chamber of Commerce was formally established. At present, there are 64 Chinese and Ukrainian-funded enterprises ' members, covering electronics, communication, engineering contracting, machinery and equipment, agriculture, logistics, tourism, law firms and other fields.
Address: stritenska st.10,Kyiv
Postal 02000
Tel: 0038-073-1540772
Email: info@cca.com.ua Website: www.cca.com. ua
(2) Ukrainian Association of Overseas Chinese Website: dciu.org.ua
Tel: 0038-068-7847929
Email: dciukraine@hotmail.com
(3) Power China Ukraine Representative Office Website: www.powerchina.cn
Address: Room 301,Lesi Ukrainky Blvd 26,Kyiv,Ukraine
Tel: 0038-050-832355
Email: yuexin@powerchina-intl.com
(4) China Building Materials International Ukraine Company Website: cnbm.com.ua/ru/
Email: office@cnbm.com.ua
(5) COFCO International Ukraine Company
Website: www.cofcointernational.com/
Address: 32-B Konovaltsa St.,Office 1019,Kyiv,Ukraine
Tel: 0038-044-2202500
Email: ivannamedvid@cofcointernational.com
(6) COSCO Shipping Ukraine Company Limited
Address: 4 Nechipurenko Lane,office 12,65045,Odessa,Ukraine
Tel: 0038-048-7340780
(7) Huawei Technology Ukraine Company Website: www.huawei.com/ua/
Address: ул. Радищева,10/14,Киев,02000
Tel: 0038-044-4987718
Email: ukraine@huawei.com
 |
 |
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
 |
 |
||
 |
|||||